Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2023
(391)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (200)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (191)
-
►
2022
(2843)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (161)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (219)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (264)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (280)
-
►
2021
(5625)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (231)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (345)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (620)
-
►
2020
(2065)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (535)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (222)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (28)
-
►
2019
(9608)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (19)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (3791)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (3737)
-
►
2018
(69720)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (3507)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (3851)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (8116)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (7758)
-
►
2017
(111579)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (7718)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (7549)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (10753)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (10529)
-
▼
2016
(16402)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (7478)
-
▼
Νοεμβρίου
(1500)
-
▼
Νοε 27
(50)
- N-acetyl cysteine in the treatment of trichotillom...
- Combination treatment of propranolol, minocycline,...
- Reduction in psoriasis related pruritus during bio...
- Morphomechanics of dermis-A method for non-destruc...
- Erratum to: An experimental study on the compariso...
- Commentary on: “An update on peripheral ossifying ...
- Targeted inhibition of WRN helicase, replication s...
- Upregulated expression of Nucleostemin/GNL3 is ass...
- A novel lab-on-chip platform with integrated solid...
- Upconversion nanoparticles grafted molybdenum disu...
- Ag/N-doped reduced graphene oxide incorporated wit...
- Acknowledgement of reviewers 2015–16
- Society News
- Issue Information
- Corrigendum to “The effect of different drugs on t...
- New multi-functional infrared materials revealed
- Roll-process technology for flexible electronics
- Preparation, morphology and superior performances ...
- Hypoxia and HIF-1 activation in bacterial infections
- Kisspeptin expression is decreased in the arcuate ...
- Giving Tuesday: Show your support this Tuesday, No...
- Microsatellite polymorphism located immediately up...
- Triolein reduces MMP-1 upregulation in dermal fibr...
- Giving Tuesday: Show your support this Tuesday, No...
- Reevaluation of MAML2 fusion–negative mucoepidermo...
- Poorly cohesive cell (diffuse-infiltrative/signet ...
- Fenestration of auricular cartilage grafts to aid ...
- Repeated otalgia at mealtimes: osteochondroma of t...
- College student marijuana involvement: Perceptions...
- Combat experience and problem drinking in veterans...
- Psychiatric disorders, suicidal ideation, and sexu...
- AMP kinase promotes Bcl6 expression in both mouse ...
- Human amniotic epithelial cells inhibit CD4+ T cel...
- AMP kinase promotes Bcl6 expression in both mouse ...
- Human amniotic epithelial cells inhibit CD4+ T cel...
- Cost effective raspberry pi-based radio frequency ...
- The effects of inter-trial interval on implicit le...
- Scapular dyskinesis among competitive swimmers
- Does Ultrasound therapy add to the effects of exer...
- A Network Analysis of DSM-5 posttraumatic stress d...
- A novel silica nanowire-silica composite aerogels ...
- Printing of highly conductive carbon nanotubes fib...
- Investigation on induction brazing of revolving he...
- Enhanced multiscale modeling of macroscopic and mi...
- A new concept of universal substitutive explosive ...
- Compressive strength prediction of nano-silica inc...
- The corrosion behavior of PCB-ImAg in industry pol...
- Direct preparation of low Ni-Cr alloy cast iron fr...
- Overexpressed PLTP in macrophage may promote chole...
- Does Complement Factor H-Related protein 5 nephrop...
-
▼
Νοε 27
(50)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (900)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (1250)
! # Ola via Alexandros G.Sfakianakis on Inoreader
Η λίστα ιστολογίων μου
Κυριακή 27 Νοεμβρίου 2016
Combination treatment of propranolol, minocycline, and tranexamic acid for effective control of rosacea
http://ift.tt/2gxnBEM
Morphomechanics of dermis-A method for non-destructive testing of collagenous tissues
Background
Collagenous tissues store, transmit and dissipate elastic energy during mechanical deformation. In skin, mechanical energy is stored during loading and then is dissipated, which protects skin from mechanical failure. Thus, energy storage (elastic properties) and dissipation (viscous properties) are important characteristics of extracellular matrices (ECMs) that support the cyclic loading of ECMs without tissue failure.
Methods
Uniaxial stress-strain measurements on decellularized human dermis have been made and compared to results of a non-destructive technique involving optical coherence tomography (OCT) combined with vibrational analysis. In addition, Poisson's ratio has been determined for tensile deformation of decellularized dermis.
Results
The modulus of decellularized dermis measured using standard tensile stress-strain tests and that determined from calculations derived from natural frequency measurements give similar results. It is also observed that Poisson's ratio for dermis is between 0.38 and 0.63 after correction for changes in volume that occur during tensile deformation. These results suggest that the assumption that dermis and other ECMs deform at constant volume is incorrect and will lead to differences in the calculated modulus by conventional tensile stress-strain measurements.
Conclusions
It is proposed that OCT in conjunction with vibrational analysis is a convenient way to non-destructively measure the modulus of decellularized dermis, ECMs and other materials that have a positive curvature to their stress-strain curves. Tensile deformation of dermis and possibly other ECMs is associated with an increase in Poisson's ratio consistent with a model of fluid expulsion from collagen fibrils during stretching. The value of Poisson's ratio should be considered in analyzing the mechanical properties of ECMs since at least dermis appears to be compressible during tensile deformation. Fluid expression during tensile deformation may play a role in mechanotransduction in skin in a similar manner to cartilage and bone tissue.
http://ift.tt/2gNBJxR
Erratum to: An experimental study on the comparison of the effects of triester glycerol oxide on wound repair
http://ift.tt/2fqz1y9
Commentary on: “An update on peripheral ossifying fibroma: case report and literature review”
http://ift.tt/2gxnuci
Targeted inhibition of WRN helicase, replication stress and cancer
Publication date: Available online 27 November 2016
Source:Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer
Author(s): Natalie Orlovetskie, Raphael Serruya, Ghada Abboud-Jarrous, Nayef Jarrous
WRN helicase has several roles in genome maintenance, such as replication, base excision repair, recombination, DNA damage response and transcription. These processes are often found upregulated in human cancers, many of which display increased levels of WRN. Therefore, directed inhibition of this RecQ helicase could be beneficial to selective cancer therapy. Inhibition of WRN is feasible by the use of small-molecule inhibitors or application of RNA interference and EGS/RNase P targeting systems. Remarkably, helicase depletion leads to a severe reduction in cell viability due to mitotic catastrophe, which is triggered by replication stress induced by DNA repair failure and fork progression arrest. Moreover, we present new evidence that WRN depletion results in early changes of RNA polymerase III and RNase P activities, thereby implicating chromatin-associated tRNA enzymes in WRN-related stress response. Combined with the recently discovered roles of RecQ helicases in cancer, current data support the targeting prospect of these genome guardians, as a means of developing clinical phases aimed at diminishing adaptive resistance to present targeted therapies.
http://ift.tt/2gABWSf
Upregulated expression of Nucleostemin/GNL3 is associated with poor prognosis and Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Publication date: Available online 27 November 2016
Source:Pathology - Research and Practice
Author(s): Lu Hua, Baoying Hu, Daliang Yan, Jinxia Liu, Yifen Shen, Fengbo Zhao, Chaoyan Shen, Buyou Chen, Xiaopeng Cui
Nucleostemin (NS)/GNL3 protein has been recently documented to be a nucleolar protein that was abundantly expressed in stem cells and cancer cells. Herein, we showed that NS was upregulated in HCC tissues and the expression of NS was inversely correlated with that of p53. Overexpression of NS predicted significantly worsened prognosis in HCC patients, suggesting that NS might serve as a prognostic marker of HCC. In addition, we found that depletion of NS sensitized HCC cells to sorafenib-induced apoptosis. Moreover, we found that the mechanism underlying NS-mediated sorafenib resistance involved dysregulated expression of p53, and downstream Bax and Bcl-2 proteins. NS interacted with p53 in HCC cells. Depletion of NS increased the expression of p53 and Bax, whereas impaired the level of cellular Bcl-2. Interference of NS enhanced the cytotoxic effects of sorafenib in HCC cells. Furthermore, ectopic expression of NS impaired the apoptosis of HCC cells following sorafenib exposure. Therefore, NS may contribute to sorafenib resistance in HCC cells through the modulation of p53 pathway and Bcl-2 proteins. These findings indicated that the combination of silencing NS expression and sorafenib treatment is a promising therapeutic strategy in treatment of HCC.
http://ift.tt/2gwSoVV
A novel lab-on-chip platform with integrated solid phase PCR and Supercritical Angle Fluorescence (SAF) microlens array for highly sensitive and multiplexed pathogen detection
Publication date: 15 April 2017
Source:Biosensors and Bioelectronics, Volume 90
Author(s): Tran Quang Hung, Wai Hoe Chin, Yi Sun, Anders Wolff, Dang Duong Bang
Solid-phase PCR (SP-PCR) has become increasingly popular for molecular diagnosis and there have been a few attempts to incorporate SP-PCR into lab-on-a-chip (LOC) devices. However, their applicability for on-line diagnosis is hindered by the lack of sensitive and portable on-chip optical detection technology. In this paper, we addressed this challenge by combining the SP-PCR with super critical angle fluorescence (SAF) microlens array embedded in a microchip. We fabricated miniaturized SAF microlens array as part of a microfluidic chamber in thermoplastic material and performed multiplexed SP-PCR directly on top of the SAF microlens array. Attribute to the high fluorescence collection efficiency of the SAF microlens array, the SP-PCR assay on the LOC platform demonstrated a high sensitivity of 1.6 copies/µL, comparable to off-chip detection using conventional laser scanner. The combination of SP-PCR and SAF microlens array allows for on-chip highly sensitive and multiplexed pathogen detection with low-cost and compact optical components. The LOC platform would be widely used as a high-throughput biosensor to analyze food, clinical and environmental samples.
Graphical abstract
http://ift.tt/2fqtWpL
Upconversion nanoparticles grafted molybdenum disulfide nanosheets platform for microcystin-LR sensing
Source:Biosensors and Bioelectronics, Volume 90
Author(s): Jiajia Lv, Sen Zhao, Shijia Wu, Zhouping Wang
Water safety is one of the most pervasive problems afflicting people throughout the world. Microcystin-LR (MC-LR), a representative toxin released by cyanobacteria, poses an increasing and serious threat to water safety. In order to develop facile, specific and sensitive detection methods for MC-LR, we fabricated an ultrasensitive fluorescence aptasensor using the enhanced fluorescence of UCNP and the effective quenching ability, high affinity toward single strand DNA (ssDNA) of MoS2 (termed as FAUM). This assay specifically determined MC-LR in the linear range of 0.01–50ng/ml with a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.002ng/ml. The real water sample results indicated that this FAUM assay owns well enough reliability and feasibility to allow the determination of MC-LR. This aptamer-based method might be a promising strategy for a variety of sensing applications.
http://ift.tt/2fquATS
Ag/N-doped reduced graphene oxide incorporated with molecularly imprinted polymer: An advanced electrochemical sensing platform for salbutamol determination
Source:Biosensors and Bioelectronics, Volume 90
Author(s): Junhua Li, Zhifeng Xu, Mengqin Liu, Peihong Deng, Siping Tang, Jianbo Jiang, Haibo Feng, Dong Qian, Lingzhi He
In this work, the metallic silver and non-metallic nitrogen co-doped reduced graphene oxide (Ag-N-RGO) was first synthesized by a simple and cost-effective strategy, and then a molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) was formed in situ at the surface of the prepared composite via electropolymerization of o-phenylenediamine in the presence of salbutamol as the template molecule. The electrochemical characterizations demonstrate that the bifunctional graphene-based composite shows improved catalytic performance than that of pristine graphene doped with one-component or none. The MIP sensor based on Ag-N-RGO owns high porous surface structure, resulting in the increased current response and enhanced recognition capacity than that of non-imprinted sensor. The outstanding performance of the developed sensor derives from the combined advantages of Ag-N-RGO with effective catalytic property and MIP with excellent selectivity. Under the optimal conditions, the electrochemical response of the developed sensor is linearly proportional to the concentration of salbutamol in the range of 0.03–20.00µmolL−1 with a low detection limit of 7 nmol L−1. The designed sensor has exhibited the multiple advantages such as low cost, simple manufacture, convenient use, excellent selectivity and good reproducibility. Finally, the proposed method has been extended for the determinations of salbutamol in human urine and pork samples, and the satisfactory recoveries between 98.9–105.3% are achieved.
http://ift.tt/2fqocwg
Society News
http://ift.tt/2gm7L0D
Issue Information
http://ift.tt/2fGSXvj
Corrigendum to “The effect of different drugs on the preparation and biological outcomes of plasma rich in growth factors” [Ann. Anat. 196 (2014) 423–429]
Source:Annals of Anatomy - Anatomischer Anzeiger
Author(s): Eduardo Anitua, María Troya, Mari Mar Zalduendo, Gorka Orive
http://ift.tt/2gNmmpv
New multi-functional infrared materials revealed
Source:Materials Today
Author(s): Laurie Donaldson
http://ift.tt/2fqp4Rl
Roll-process technology for flexible electronics
Source:Materials Today
Author(s): Laurie Donaldson
http://ift.tt/2gxalAg
Preparation, morphology and superior performances of biobased thermoplastic elastomer by in situ dynamical vulcanization for 3D-printed materials
Publication date: 13 January 2017
Source:Polymer, Volume 108
Author(s): Xiaoran Hu, Hailan Kang, Yan Li, Yiting Geng, Runguo Wang, Liqun Zhang
3D-printing of polymers provides the opportunity to fabricate materials into customized sizes and shapes. The present study describes fully renewable thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) consisting of synthesized biobased elastomer (PLBSI) and poly (lactic acid) (PLA) by in situ dynamic vulcanization for 3D-printed materials. The morphology study implied in situ dynamic vulcanization and phase inversion occurs and leads the PLBSI elastomer dispersed as microparticles in PLA matrix. Then, the morphological evolution mechanism was proposed and indicated the dispersed PLBSI elastomer microparticles are actually agglomerates of elastomer nanoparticles. The PLBSI/PLA TPVs perform good processability and reprocessability by rheological and recyclability tests. Besides, good in vitro degradability and cytotoxicity suggests PLBSI/PLA TPVs are promising sustainable biomaterials. The superior strength and elasticity confirmed by the tensile tests of 3D-printed samples, and firm microstructure and the reliable printed accuracy of 3D-printed samples investigated by SEM implied the PLBSI/PLA TPVs were ideal 3D-printing materials.
Graphical abstract
http://ift.tt/2fqdJAW
Hypoxia and HIF-1 activation in bacterial infections
Source:Microbes and Infection
Author(s): Gayatri Devraj, Christiane Beerlage, Bernhard Brüne, Volkhard A.J. Kempf
For most of the living being, oxygen is one of the essential elements required to sustain life. Deprivation of oxygen causes tissue hypoxia and this affects host cell and organ functions severely. Tissue hypoxia is a prominent microenvironmental condition occurring in infections and there is a body of evidence that hypoxia and inflammation are interconnected with each other. The primary key factor mediating the mammalian hypoxic response is hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1, which regulates oxygen homeostasis on cellular, tissue and organism levels. Recent studies show that HIF-1 plays a central role in angiogenesis, cancer and cardiovascular disease but also in bacterial infections. Activation of HIF-1 depends on the nature of the pathogen and the characteristics of particular infections in certain hosts. Up to date, it is not completely clear whether the phenomenon of HIF-1 activation in infections has a protective or detrimental effect for the host. In this review, we give an overview whether and how hypoxia and HIF-1 affect the course of infections.
http://ift.tt/2gwz7Uy
Kisspeptin expression is decreased in the arcuate nucleus of hypothyroid female rats with irregular estrus cycles
Source:Neuroscience Research
Author(s): Yuji Tomori, Ken Takumi, Norio Iijima, Shinro Takai, Hitoshi Ozawa
Insufficiency of thyroid hormones inhibits gonadotropin release and results in dysregulation of reproductive function, although the precise mechanism of this disrupted gonadotropin secretion remains unclear. Kisspeptin is a neuropeptide that strongly stimulates gonadotropin secretion and plays an important role in reproductive function. To examine the involvement of kisspeptin in the dysregulation of gonadotropin secretion in hypothyroidism, we investigated Kiss1 mRNA expression and kisspeptin immunoreactivity in the hypothalamus of female rats treated with propylthiouracil (PTU). In the PTU-treated rats, serum thyroxine (T4) was significantly decreased, whereas thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) levels were significantly increased. In addition, irregular estrus cycles were observed in PTU-treated rats. In situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry revealed significant reductions in the number of Kiss1 mRNA-expressing neurons and kisspeptin-immunoreactive neurons in the arcuate nucleus (ARC) but not in the anteroventral periventricular nucleus (AVPV) of the PTU-treated rats. Although the serum levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and estradiol (E2) were unaffected, serum prolactin levels were significantly increased after PTU treatment. These data indicate that kisspeptin expression in the ARC is suppressed under thyroid hormone insufficiency, suggesting that the dysregulation of reproductive function in hypothyroidism is caused by inhibition of kisspeptin neurons in the ARC.
http://ift.tt/2gwYmmk
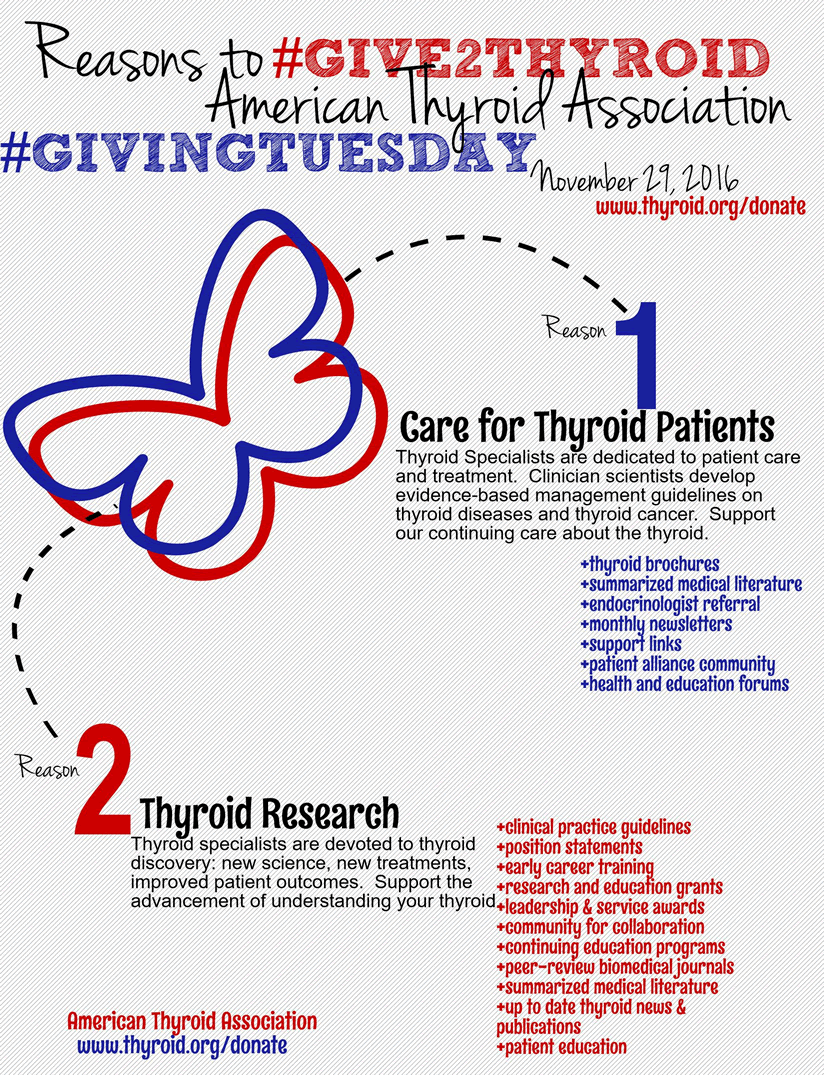
Giving Tuesday: Show your support this Tuesday, November 29, 2016
#GivingTuesday is a global day of giving fueled by the power of social media and collaboration. Celebrated on the Tuesday following Thanksgiving (in the U.S.) and the widely recognized shopping events Black Friday and Cyber Monday, #GivingTuesday kicks off the charitable season, when many focus on their holiday and end-of-year giving. Help support the Thyroid Association by contributing to our #GivingTuesday fundraiser during the month of November!
The post Giving Tuesday: Show your support this Tuesday, November 29, 2016 appeared first on American Thyroid Association.
http://ift.tt/2gw2YfX
Microsatellite polymorphism located immediately upstream of the phosphatidylinositol glycan, class K gene (PIGK) affects its expression, which correlates with tyrosinase activity in human melanocytes
Publication date: Available online 27 November 2016
Source:Journal of Dermatological Science
Author(s): Ken Okamura, Masahiro Hayashi, Yuko Abe, Yuta Araki, Yutaka Hozumi, Tamio Suzuki
http://ift.tt/2fUe2jy
Triolein reduces MMP-1 upregulation in dermal fibroblasts generated by ROS production in UVB-irradiated keratinocytes
Publication date: Available online 27 November 2016
Source:Journal of Dermatological Science
Author(s): Gustavo J. Leirós, Ana Gabriela Kusinsky, María Eugenia Balañá, Karin Hagelin
BackgroundCytokine production and oxidative stress generated by ultraviolet radiation B (UVB) skin exposure are main factors of skin photoaging. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) produced by irradiated keratinocytes is proposed to have a role in metalloproteinases (MMPs) expression activation in dermal fibroblasts.ObjectivesWe examined the effect of triolein treatment of UVB-irradiated keratinocytes on MMP1 (interstitial collagenase) expression response of dermal fibroblasts. We assayed UVB-irradiated keratinocytes soluble signals, mainly IL-6 and reactive oxygen species (ROS).MethodsIL-6 expression and ROS generation were assayed in UVB-irradiated keratinocytes. MMP1 mRNA expression response was assayed in fibroblasts grown in keratinocytes conditioned medium. We evaluated the effect of treating keratinocytes with triolein on IL-6 expression and ROS generation in keratinocytes, and MMP1 expression in fibroblasts.ResultsThe irradiation of epidermal cells with sublethal UVB doses increased IL-6 expression and ROS generation. Conditioned culture medium collected from keratinocytes was used to culture dermal fibroblasts. MMP1 mRNA expression increase was observed in fibroblasts cultured in medium collected from UVB-irradiated keratinocytes. Triolein treatment reduced the IL-6 expression and ROS generation in keratinocytes and this effect was reflected in downregulation of MMP1 expression in fibroblasts.ConclusionsTriolein reduces both the expression of IL-6 and ROS generation in irradiated keratinocytes. It seems to exert an anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative stress effect on irradiated keratinocytes that in turn reduces MMP1 expression in dermal fibroblasts. Collectively, these results indicate that triolein could act as a photoprotective agent.
http://ift.tt/2g8kt5A
Giving Tuesday: Show your support this Tuesday, November 29, 2016
#GivingTuesday is a global day of giving fueled by the power of social media and collaboration. Celebrated on the Tuesday following Thanksgiving (in the U.S.) and the widely recognized shopping events Black Friday and Cyber Monday, #GivingTuesday kicks off the charitable season, when many focus on their holiday and end-of-year giving. Help support the Thyroid Association by contributing to our #GivingTuesday fundraiser during the month of November!
The post Giving Tuesday: Show your support this Tuesday, November 29, 2016 appeared first on American Thyroid Association.
http://ift.tt/2gw2YfX
Reevaluation of MAML2 fusion–negative mucoepidermoid carcinoma: a subgroup being actually hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma of the salivary gland with EWSR1 translocation
Publication date: March 2017
Source:Human Pathology, Volume 61
Author(s): Min-Shu Hsieh, Hsuang Wang, Yi-Hsuan Lee, Jenq-Yuh Ko, Yih-Leong Chang
Hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma (HCCC) is a rare salivary gland tumor with a specific EWSR1-ATF1 fusion gene and can have mucin production. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC) with a clear cell component is its morphologic mimic. Using MAML2 fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), a total of 49 MEC cases were separated into MAML2 fusion–positive (32 cases) and MAML2 fusion–negative groups (17 cases). This study used EWSR1 FISH to investigate MAML2 fusion–negative cases to identify previously unrecognized HCCC. Among 17 MAML2 fusion–negative cases, 3 had rearrangement of the EWSR1 gene and were reclassified as HCCC. Including 5 previously diagnosed HCCC cases, these 8 HCCC cases had a male-to-female ratio of 1:7, and most (7/8) tumors arose from oral minor salivary glands in the oral cavity (tongue base and palate). EWSR1-ATF1 fusion was confirmed by FISH in all 8 HCCC cases. The histologic features between genetically confirmed HCCC and MEC were compared. HCCC was significantly associated with minor salivary gland involvement, a discrepancy between low-grade cytology and intermediate- to high-grade histology using the MEC grading system, and absence of both epidermoid cells with abundant cytoplasm and goblet cells lining cysts or forming clusters. Clear cells and a hyalinized stroma were not specific for HCCC. HCCC may be erroneously classified as MEC because clear cells may be a minor histologic component and mucin production is not uncommon. Previously diagnosed MEC cases should be reevaluated, especially those arising from minor salivary glands or without MAML2 fusion. Careful histologic evaluation with supporting molecular testing can facilitate pathologic diagnoses.
http://ift.tt/2gMZKoW
Poorly cohesive cell (diffuse-infiltrative/signet ring cell) carcinomas of the gallbladder: clinicopathological analysis of 24 cases identified in 628 gallbladder carcinomas
Publication date: February 2017
Source:Human Pathology, Volume 60
Author(s): Deniz Tuncel, Juan Carlos Roa, Juan Carlos Araya, Enrique Bellolio, Miguel Villaseca, Oscar Tapia, Kee-Taek Jang, Brian Quigley, Burcu Saka, Olca Basturk, Juan Sarmiento, Hector F. Losada, Samip Patel, Michelle D. Reid, Bahar Memis, Volkan Adsay
http://ift.tt/2gAbloj
Fenestration of auricular cartilage grafts to aid healing of alar wounds by secondary intention
Alar reconstruction should follow the principles of cosmetic subunits for nasal reconstruction,1 so defects that affect multiple subunits (Fig. 1) should be converted into a single alar defect (Fig. 2). The contralateral ala is used as the template to recreate a symmetrical and appropriately positioned alar groove. The purpose of the cartilage graft is twofold: to preserve the patency of the internal valve, and to prevent contraction caused by the formation of granulation tissue during healing. Patency of the nasal valve may be assessed using the Cottle test,2 and from observing the nostrils from below (preoperatively).
http://ift.tt/2glfOdU
Repeated otalgia at mealtimes: osteochondroma of the mandibular condyle
Referred otalgia is sometimes misdiagnosed as tension headache or migraine. Clinicians can easily overlook these disorders, and request unnecessary and expensive investigations. Secondary otalgia caused by osteochondroma of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) can be a difficult to diagnose for even experienced oral and maxillofacial (OMF) surgeons.
http://ift.tt/2fpo4Nk
College student marijuana involvement: Perceptions, use, and consequences across 11 college campuses
Source:Addictive Behaviors, Volume 66
Author(s): Matthew R. Pearson, Bruce S. Liese, Robert D. Dvorak
BackgroundMarijuana is currently the most commonly used illicit drug in the United States, and with the movement toward legalization of recreational marijuana, the country faces numerous issues regarding policy, prevention, and treatment of marijuana use. The present study examines the prevalence of marijuana use and consequences and compares users and non-users on a wide range of other marijuana-related constructs among college students across 11 universities.MethodParticipants included 8141 college students recruited from the psychology department participant pools of 11 universities throughout the US, including four major regions of the US (West, South, Midwest, Northeast) and states with varying policies regarding the legality of marijuana use.ResultsWe observed marijuana use rates similar to representative samples of young adults and college students (i.e., 53.3% lifetime marijuana users, 26.2% past month marijuana users). About 1 in 10 past month marijuana users experienced no consequences from their use, whereas nearly 1 in 10 experienced 19 or more consequences. Lifetime marijuana users had more positive perceptions of marijuana compared to non-users on a wide-range of marijuana-related constructs.ConclusionsWe report descriptive statistics on a wide range of marijuana-related variables. We hope that these data provide a useful baseline prior to increased legalization of recreational marijuana use. Multi-site studies like this one are needed to study the risky and protective factors for problematic marijuana use. These findings can inform interventions and public policy.
http://ift.tt/2gvRJEu
Combat experience and problem drinking in veterans: Exploring the roles of PTSD, coping motives, and perceived stigma
Source:Addictive Behaviors, Volume 66
Author(s): Stephen M. Miller, Eric R. Pedersen, Grant N. Marshall
PurposeThe current investigation sought to illustrate the etiology of adverse alcohol consequences in young adult veterans using a path analytic framework.MethodsA total of 312 veterans aged 19–34 were enrolled in a larger intervention study on alcohol use. At baseline, participants completed measures of combat severity, PTSD symptom severity, and drinking motives to cope. At one month follow-up, participants completed measures of perceived stigma of behavioral health treatment seeking and past 30-day alcohol consequences.ResultsAfter entering the covariates of age, gender, race/ethnicity, and past year behavioral health treatment utilization, a path analytic model demonstrated a good fit to the data predicting alcohol consequences in this population. Further, a separate exploratory analysis confirmed that both drinking motives to cope and perceived stigma of behavioral health treatment seeking mediated the link between PTSD symptom severity and alcohol consequences.ConclusionsThe current model expands upon prior research showing the relationship between combat severity and alcohol use behavior in young adult veterans. Results support the notion that veterans with PTSD symptoms may drink to cope and that perceived stigma surrounding help seeking may further contribute to alcohol related problems.
http://ift.tt/2fCmLWo
Psychiatric disorders, suicidal ideation, and sexually transmitted infections among post-deployment veterans who utilize digital social media for sexual partner seeking
Source:Addictive Behaviors, Volume 66
Author(s): Jack L. Turban, Marc N. Potenza, Rani A. Hoff, Steve Martino, Shane W. Kraus
IntroductionDigital social media platforms represent outlets through which individuals may find partners for sexual encounters. Using a sample of US post-deployment military veterans, the current study evaluated the prevalence of digital sex seeking as well as clinical correlates of psychopathology, suicidal ideation, and sexually transmitted infections (STIs).MethodsUsing data from a baseline telephone interview and follow-up internet-based survey, we examined the prevalence of sexual partnering via digital social media platforms in a national sample of 283 US combat veterans.ResultsAmong veterans, 35.5% of men and 8.5% of women reported having used digital social media to meet someone for sex. Individuals who reported having used digital social media to find sexual partners (DSMSP+) as compared to those who did not (DSMSP-) were more likely to be young, male, and in the Marine Corps. After adjusting for sociodemographic variables, DSMSP+ status was associated with post-traumatic stress disorder (OR=2.26, p=0.01), insomnia (OR=1.99, p=0.02), depression (OR=1.95, p=0.03), hypersexuality (OR=6.16, p<0.001), suicidal ideation (OR=3.24, p=0.04), and treatment for an STI (OR=1.98, p=0.04).ConclusionAmong US post-deployment military veterans, DSMSP+ behaviors were prevalent, particularly among men. The association between DSMSP+ behaviors and PTSD, insomnia, depression, hypersexuality, suicidal ideation, and STIs suggest that veterans who engage in DSMSP+ behaviors should be particularly thoroughly screened and evaluated for these psychiatric concerns and counseled on the benefits of safe sexual practices.
http://ift.tt/2fClLBS
AMP kinase promotes Bcl6 expression in both mouse and human T cells
Source:Molecular Immunology, Volume 81
Author(s): Markus M. Xie, Tohti Amet, Hong Liu, Qigui Yu, Alexander L. Dent
The transcription factor Bcl6 is a master regulator of follicular helper T (TFH) cells, and understanding the signaling pathway that induces Bcl6 and TFH cell differentiation is therefore critical. IL-2 produced during T cell activation inhibits Bcl6 expression but how TFH cells evade IL-2 inhibition is not completely understood. Here we show that Bcl6 is highly up-regulated in activated CD4 T cells following glucose deprivation (GD), and this pathway is insensitive to inhibition by IL-2. Similar to GD, the glucose analog 2-deoxyglucose (2DG) inhibits glycolysis, and 2DG induced Bcl6 expression in activated CD4 T cells. The metabolic sensor AMP kinase (AMPK) is activated when glycolysis is decreased, and the induction of Bcl6 by GD was inhibited by the AMPK antagonist compound C. Additionally, activation of AMPK by the drug AICAR caused Bcl6 up-regulation in activated CD4 T cells. When mice were immunized with KLH using AICAR as an adjuvant, there was a strong TFH–dependent enhancement of KLH-specific antibody (Ab) responses, and higher Bcl6 expression in TFH cells in vivo. Activation of AMPK strongly induced BCL6 and the up-regulation of TFH cell marker expression by human CD4 T cells. Our data reveal a major new pathway for TFH cell differentiation, conserved by both mouse and human T cells. Mature TFH cells are reported to have a lower metabolic state compared to TH1 cells. Our data indicates that decreased metabolism may be deterministic for TFH cell differentiation, and not simply a result of TFH cell differentiation.
http://ift.tt/2fFwij3
Human amniotic epithelial cells inhibit CD4+ T cell activation in acute kidney injury patients by influencing the miR-101-c-Rel-IL-2 pathway
Publication date: January 2017
Source:Molecular Immunology, Volume 81
Author(s): Junfeng Liu, Rong Hua, Zhangbin Gong, Bin Shang, Yongyi Huang, Lihe Guo, Te Liu, Jun Xue
In the pathogenesis of acute kidney injury (AKI), the release of multiple interleukins can lead to increased kidney damage. Human amniotic epithelial cells (HuAECs) can inhibit immune cell activation in vivo and in vitro. We hypothesized that HuAECs could weaken patient-derived peripheral blood CD4+ T-cell activation and decreasing the ability of these cells to express and release IL-2. −Cell proliferation assay revealed that under the same culture conditions, activated AKI patient-derived CD4+ T cells had a significantly reduced proliferation rate when were co-cultured with HuAECs. And the level of IL-2 released was also significantly reduced. Western blot and qRT-PCR assays showed that the expression of c-Rel in the CD4+ T cells was also significantly reduced. However, the expression level of endogenous miR-101 in the CD4+ T cells co-cultured with HuAECs was significantly increased. Luciferase reporter assay results suggested that miR-101 could bind to a specific site in the c-Rel 3′ UTR and induce the post-transcriptional silencing of c-Rel. Subsequently, we over-expressed miR-101 in AKI patient-derived CD4+ T cells. The qRT-PCR and western blot assay results revealed that the expression of endogenous c-Rel was significantly reduced, while the ELISA results indicated that the level of IL-2 released was also significantly decreased. Finally, ChIP-PCR assay results showed that the miR-101-overexpressing CD4+ T-cell group and the HuAEC co-culture CD4+ T-cell group exhibited significantly decreased binding capacities between the 'c-Rel-NFκB' complex and the IL-2 gene promoter, and the transcriptional activity of IL-2 was also significantly decreased. Therefore, we confirmed that HuAECs can stimulate miR-101 expression in AKI patient-derived peripheral blood CD4+ T cells, thus inhibiting the expression of the miR-101 target gene c-Rel and leading to a reduction in IL-2 expression and release.
http://ift.tt/2fFAL5l
AMP kinase promotes Bcl6 expression in both mouse and human T cells
Source:Molecular Immunology, Volume 81
Author(s): Markus M. Xie, Tohti Amet, Hong Liu, Qigui Yu, Alexander L. Dent
The transcription factor Bcl6 is a master regulator of follicular helper T (TFH) cells, and understanding the signaling pathway that induces Bcl6 and TFH cell differentiation is therefore critical. IL-2 produced during T cell activation inhibits Bcl6 expression but how TFH cells evade IL-2 inhibition is not completely understood. Here we show that Bcl6 is highly up-regulated in activated CD4 T cells following glucose deprivation (GD), and this pathway is insensitive to inhibition by IL-2. Similar to GD, the glucose analog 2-deoxyglucose (2DG) inhibits glycolysis, and 2DG induced Bcl6 expression in activated CD4 T cells. The metabolic sensor AMP kinase (AMPK) is activated when glycolysis is decreased, and the induction of Bcl6 by GD was inhibited by the AMPK antagonist compound C. Additionally, activation of AMPK by the drug AICAR caused Bcl6 up-regulation in activated CD4 T cells. When mice were immunized with KLH using AICAR as an adjuvant, there was a strong TFH–dependent enhancement of KLH-specific antibody (Ab) responses, and higher Bcl6 expression in TFH cells in vivo. Activation of AMPK strongly induced BCL6 and the up-regulation of TFH cell marker expression by human CD4 T cells. Our data reveal a major new pathway for TFH cell differentiation, conserved by both mouse and human T cells. Mature TFH cells are reported to have a lower metabolic state compared to TH1 cells. Our data indicates that decreased metabolism may be deterministic for TFH cell differentiation, and not simply a result of TFH cell differentiation.
http://ift.tt/2fFwij3
Human amniotic epithelial cells inhibit CD4+ T cell activation in acute kidney injury patients by influencing the miR-101-c-Rel-IL-2 pathway
Publication date: January 2017
Source:Molecular Immunology, Volume 81
Author(s): Junfeng Liu, Rong Hua, Zhangbin Gong, Bin Shang, Yongyi Huang, Lihe Guo, Te Liu, Jun Xue
In the pathogenesis of acute kidney injury (AKI), the release of multiple interleukins can lead to increased kidney damage. Human amniotic epithelial cells (HuAECs) can inhibit immune cell activation in vivo and in vitro. We hypothesized that HuAECs could weaken patient-derived peripheral blood CD4+ T-cell activation and decreasing the ability of these cells to express and release IL-2. −Cell proliferation assay revealed that under the same culture conditions, activated AKI patient-derived CD4+ T cells had a significantly reduced proliferation rate when were co-cultured with HuAECs. And the level of IL-2 released was also significantly reduced. Western blot and qRT-PCR assays showed that the expression of c-Rel in the CD4+ T cells was also significantly reduced. However, the expression level of endogenous miR-101 in the CD4+ T cells co-cultured with HuAECs was significantly increased. Luciferase reporter assay results suggested that miR-101 could bind to a specific site in the c-Rel 3′ UTR and induce the post-transcriptional silencing of c-Rel. Subsequently, we over-expressed miR-101 in AKI patient-derived CD4+ T cells. The qRT-PCR and western blot assay results revealed that the expression of endogenous c-Rel was significantly reduced, while the ELISA results indicated that the level of IL-2 released was also significantly decreased. Finally, ChIP-PCR assay results showed that the miR-101-overexpressing CD4+ T-cell group and the HuAEC co-culture CD4+ T-cell group exhibited significantly decreased binding capacities between the 'c-Rel-NFκB' complex and the IL-2 gene promoter, and the transcriptional activity of IL-2 was also significantly decreased. Therefore, we confirmed that HuAECs can stimulate miR-101 expression in AKI patient-derived peripheral blood CD4+ T cells, thus inhibiting the expression of the miR-101 target gene c-Rel and leading to a reduction in IL-2 expression and release.
http://ift.tt/2fFAL5l
Cost effective raspberry pi-based radio frequency identification tagging of mice suitable for automated in vivo imaging
Source:Journal of Neuroscience Methods
Author(s): Federico Bolaños, Jeff M LeDue, Timothy H Murphy
BackgroundAutomation of animal experimentation improves consistency, reduces potential for error while decreasing animal stress and increasing well-being. Radio frequency identification (RFID) tagging can identify individual mice in group housing environments enabling animal-specific tracking of physiological parameters.New methodWe describe a simple protocol to radio frequency identification (RFID) tag and detect mice. RFID tags were injected sub-cutaneously after brief isoflurane anesthesia and do not require surgical steps such as suturing or incisions. We employ glass-encapsulated 125kHz tags that can be read within 30.2±2.4mm of the antenna. A raspberry pi single board computer and tag reader enable automated logging and cross platform support is possible through Python.ResultsWe provide sample software written in Python to provide a flexible and cost effective system for logging the weights of multiple mice in relation to pre-defined targets.Comparison with existing methodsThe sample software can serve as the basis of any behavioral or physiological task where users will need to identify and track specific animals. Recently, we have applied this system of tagging to automated mouse brain imaging within home-cages.ConclusionsWe provide a cost effective solution employing open source software to facilitate adoption in applications such as automated imaging or tracking individual animal weights during tasks where food or water restriction is employed as motivation for a specific behavior.
http://ift.tt/2gvsm5x
The effects of inter-trial interval on implicit learning of sequential visual isometric pinch task
Publication date: Available online 27 November 2016
Source:Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies
Author(s): Fahimeh Hashemirad, Paul B. Fitzgerald, Maryam Zoghi, Masoumeh Hashemirad, Shapour Jaberzadeh
Sequential visual isometric pinch task (SVIPT) has been recently used as a visuomotor sequence task in clinical research. The influence of varying intervals between sequenced trials on the acquisition of implicit sequence learning is not yet determined for SVIPT. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of inter-trial interval (ITI) on implicit motor sequence learning using SVIPT. A total of 32 healthy participants with mean age 31.3 ± 4.5 years participated in this study. Participants were randomly assigned to one of four ITI groups; (1, 2, 3 and 4 sec). They were instructed to control their force on a force transducer to reach a number of targets which appeared on the computer screen by changing the pinch force exerted onto the transducer. In this study, outcome measures were movement time, error rate and skill, which were measured before and after training. Our results indicated that motor sequence learning similarly affected various ITIs. Indeed, all participants exhibited same improvement in implicit learning of SVIPT even though the ITIs varied from 1 to 4 sec. Our findings suggest that implicit learning of SVIPT is independent of ITI within this range in healthy individuals.
http://ift.tt/2fBILkg
Scapular dyskinesis among competitive swimmers
Publication date: Available online 27 November 2016
Source:Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies
Author(s): Maayan Bussiba Maor, Tatyana Ronin, Leonid Kalichman
AimTo evaluate the prevalence of scapular dyskinesis (SD) in competitive swimmers during training sessions.MethodsRepeated measurement observational study.20 young competitive swimmers were filmed before, at midpoint and at the end of a training session, performing shoulder flexion and abduction. SD was examined separately by two assessors. Demographic and Quick Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand questionnaires were collected.ResultsSD was observed in 30% of the swimmers before training, in 70%, an hour later, and in 80%, upon completion of the training session. The difference between the baseline and mid-practice was close to significance (p-value = 0.055), and between mid-practice and end of practice was significant (p = 0.004).ConclusionsThis study confirmed that the prevalence of SD increases throughout a training session in most swimmers. The main reason might be fatigue of the muscles which stabilize the scapula, therefore, when examining a sportsmen's shoulder, it is important to examine the SD post-training or following simulation of the training session in the clinic.
http://ift.tt/2gvh7dx
Does Ultrasound therapy add to the effects of exercise and mobilization in frozen shoulder? A pilot randomized double-blind clinical trial
Publication date: Available online 27 November 2016
Source:Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies
Author(s): Safoora Ebadi, Bijan Forogh, Ehsan Fallah, Arash Babaei Ghazani
ObjectiveThis study intended to determine the extent to which Ultrasound could add to the effects of exercise and manual therapy in the rehabilitation treatment of primary adhesive capsulitis.DesignA pilot double blind randomized clinical trial was carried out on 50 patients suffering from primary adhesive capsulitis. Intervention included continuous 3 MHz, 1.5 w/cm2 Ultrasound, applied for the first group and sham Ultrasound for the second group. In addition specific stretching and strengthening exercises as well as glenohumeral joint mobilization were delivered to both groups. Pain (VAS), functional ability (using Oxford Shoulder Score) and shoulder range of motion were assessed at the baseline, after 10 sessions of treatment, and at 3 months follow-up. An intention to treat Mixed ANOVA analysis was performed to explore the interaction effects of time and group on outcome measures.ResultsNo significant interaction effect of time and group was seen on pain, function and Range of Motion (p>.05), meaning that the amount of improvement in all outcome measures were alike in the two groups.ConclusionApplying continuous Ultrasound along with a regimen of semi supervised exercise and mobilization in patients with primary adhesive capsulitis did not have any additional effect to the placebo Ultrasound, on outcome measures. Larger scale studies are needed to confirm the findings.
http://ift.tt/2fBKpCE
A Network Analysis of DSM-5 posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms and correlates in U.S. military veterans
Source:Journal of Anxiety Disorders
Author(s): Cherie Armour, Eiko I. Fried, Marie K. Deserno, Jack Tsai, Robert H. Pietrzak
ObjectiveRecent developments in psychometrics enable the application of network models to analyze psychological disorders, such as PTSD. Instead of understanding symptoms as indicators of an underlying common cause, this approach suggests symptoms co-occur in syndromes due to causal interactions. The current study has two goals: (1) examine the network structure among the 20 DSM-5 PTSD symptoms, and (2) incorporate clinically relevant variables to the network to investigate whether PTSD symptoms exhibit differential relationships with suicidal ideation, depression, anxiety, physical functioning/quality of life (QoL), mental functioning/QoL, age, and sex.MethodWe utilized a nationally representative U.S. military veteran's sample; and analyzed the data from a subsample of 221 veterans who reported clinically significant DSM-5 PTSD symptoms. Networks were estimated using state-of-the-art regularized partial correlation models. Data and code are published along with the paper.ResultsThe 20-item DSM-5 PTSD network revealed that symptoms were positively connected within the network. Especially strong connections emerged between nightmares and flashbacks; blame of self or others and negative trauma-related emotions, detachment and restricted affect; and hypervigilance and exaggerated startle response. The most central symptoms were negative trauma-related emotions, flashbacks, detachment, and physiological cue reactivity. Incorporation of clinically relevant covariates into the network revealed paths between self-destructive behavior and suicidal ideation; concentration difficulties and anxiety, depression, and mental QoL; and depression and restricted affect.ConclusionThese results demonstrate the utility of a network approach in modeling the structure of DSM-5 PTSD symptoms, and suggest differential associations between specific DSM-5 PTSD symptoms and clinical outcomes in trauma survivors. Implications of these results for informing the assessment and treatment of this disorder, are discussed.
http://ift.tt/2gLYC4X
A novel silica nanowire-silica composite aerogels dried at ambient pressure
Publication date: 5 February 2017
Source:Materials & Design, Volume 115
Author(s): Xiaobing Tang, Aihua Sun, Chengyi Chu, Mingli Yu, Si Ma, Yuchuan Cheng, Jianjun Guo, Gaojie Xu
A novel silica nanowire-silica composite aerogels with excellent thermal insulation and mechanical properties was prepared by adding SiO2 nanowires as a secondary phase into the silica matrix and drying at ambient pressure. The SiO2 nanowires and silica aerogel matrix have outstanding compatibility and dispersibility because the components of nanowire and aerogel matrix all are silica, which contributes to the improvement of the mechanical property of the silica composite aerogels. The physical, mechanical and thermal properties of the SiO2 nanowires based composite silica aerogel are investigated and discussed in detail. The results indicate that the monolithic aerogels with high specific surface area, porosity and large pore volume. The thermal conductivity of the composite silica aerogels only increases gently (0.006W·m−1K−1) as the addition of SiO2 nanowires rises from 0wt% to 14wt%, while their mechanical properties have been improved greatly. The SiO2 nanowires based composite silica aerogel would be widely used in the thermal insulation application because of its outstanding thermal insulation property.
Graphical abstract
http://ift.tt/2fo21Xl
Printing of highly conductive carbon nanotubes fibres from aqueous dispersion
Publication date: 15 February 2017
Source:Materials & Design, Volume 116
Author(s): Dawid Janas, Stefanie K. Kreft, Krzysztof K.K. Koziol
Carbon nanotubes (CNT) fibres were printed from liquid suspension. The resulting fibres are highly conductive, with conductivity close to the one of standard CNT fibres, flexible and very versatile. The printed fibres are comparable to fibres that can be gained from direct spinning, carpet spinning and spinning from superacids, but offer broader range of composition and are simpler and safer to produce as no high-temperature equipment and dangerous chemicals need to be used. Any CNT material can be implemented, allowing the use of a variety of CNT structures, different densities of the fibres and various shapes for the final product.
Graphical abstract
http://ift.tt/2fnZHzA
Investigation on induction brazing of revolving heat pipe grinding wheel
Publication date: 15 February 2017
Source:Materials & Design, Volume 116
Author(s): Jiajia Chen, Yucan Fu, Qilin Li, Junjie Gao, Qingshan He
Revolving heat pipe grinding wheel (RHPGW) has been proposed to realize dry grinding of difficult-to-machine materials. The RHPGW has a variable wall thickness with a thinnest part of 1.5mm along the width direction. This investigation aims at developing an induction brazing method for RHPGW in order to prevent deformation, improve the inter-chip space, and achieve uniform grit distribution. Simulations were performed on FLUX to design a suitable induction coil and the related working parameters. Ag-Cu-Ti alloy and CBN grains were applied in the brazing experiments. The brazing temperature, geometric accuracy, microstructure and the compounds at the matrix/Ag-Cu-Ti/CBN interface were analyzed along the width direction, good consistency was achieved for different positions. Further validation experiments were carried out by dry grinding of Inconel 718 and compared with the results ground by electroplated RHPGW. Lower grinding forces and higher service life was obtained with the induction brazed RHPGW. Abrasion wear was found to be the main failure mode for the brazed grinding wheel, while both significant adhesion and wear were the failure forms for the electroplate one.
Graphical abstract
http://ift.tt/2fnY0Cs
Enhanced multiscale modeling of macroscopic and microscopic residual stresses evolution during multi-thermo-mechanical processes
Publication date: 5 February 2017
Source:Materials & Design, Volume 115
Author(s): X.X. Zhang, D. Wang, B.L. Xiao, H. Andrä, W.M. Gan, M. Hofmann, Z.Y. Ma
After several decades, it is still difficult to predict "macroscopic and microscopic (M-m)" residual stresses (RSes) in metal matrix composites (MMCs) after welding. In this work, an enhanced multiscale model is developed to predict the evolution of M-m RSes in MMCs during several thermo-mechanical processes including welding. This multiscale model is capable of handling non-zero initial M-m RSes and integrates the temperature history dependent constitutive model (THDCM) at both macroscale and microscale. Meanwhile, thermal source model of friction stir welding (FSW) is integrated. The extension to other welding thermal source is straightforward. This multiscale model is used to study the generation, inheritance, and evolution of M-m RSes in a SiC/Al composite during quenching, FSW and post-welding heat treatment (PWHT). The effects of initial M-m RSes and material constitutive models on the prediction of M-m RSes are systematically assessed. It is found that using the THDCM and taking into account the initial RSes, this multiscale model shows the best predictions of RSes in the FSW joint of MMCs. The predictions agree with the neutron diffraction measurements reasonably well. It is found that the reduction of RSes during PWHT is mainly caused by the stress relaxation during the solution treatment stage.
Graphical abstract
http://ift.tt/2fo0fW7
A new concept of universal substitutive explosive welding
Publication date: 5 February 2017
Source:Materials & Design, Volume 115
Author(s): C. Choi, P. Tan, D. Ruan, B. Dixon
This paper presents an innovative explosive welding technology, namely Universal Substitutive Explosive Welding technique, which was recently developed by Australian Defence Science and Technology Group to improve the survivability and mobility of military vehicles. The new technique is superior to the existing industrial explosive welding ones in terms of integrity, quality and stability. It is able to significantly upgrade the hardness upper limit of target material and ensure the perfect welding bond between the flyer (soft) and target (hard) panels without size limitation of target panel. Experimental results show that using the new technique raised the ballistic velocity limit (V50) of the explosively welded panel by up to 20% and reduced the bulge depth (related to dynamic plasticity) significantly without any rupture or fragmentation issues. Charpy impact test on the sample fabricated by the new technique showed strong recovery effects with time with no transition temperature.
Graphical abstract
http://ift.tt/2fnZPzg
Compressive strength prediction of nano-silica incorporated cement systems based on a multiscale approach
Publication date: 5 February 2017
Source:Materials & Design, Volume 115
Author(s): Madhuwanthi Rupasinghe, Priyan Mendis, Tuan Ngo, Tuan Ngoc Nguyen, Massoud Sofi
Effect on strength characteristics of nano-engineered concrete when cement content is replaced with nano-silica at small replacement levels is analysed experimentally and numerically in this paper. The reactivity of nano-silica within the cement paste is quantified through investigating microstructural images of cement pastes. A multiscale finite element model based on quantification of microstructural image analysis is developed to predict the compressive strength of the nano-modified system. Representative Volume Elements (RVEs) of the cement/nano-silica systems are developed at three different length scales; for the micro-level, meso-level and macro-level. Experimental analyses conducted for cement paste, mortar and concrete are used to validate the model predictions. The numerical modelling and experimental investigations reveal that the optimum replacement content of cement with nano-silica is around 8wt% for maximum strength enhancement.
Graphical abstract
http://ift.tt/2fo4CjS
The corrosion behavior of PCB-ImAg in industry polluted marine atmosphere environment
Publication date: 5 February 2017
Source:Materials & Design, Volume 115
Author(s): Lidan Yan, Kui Xiao, Pan Yi, Chaofang Dong, Junsheng Wu, Ziheng Bai, Chengliang Mao, Li Jiang, Xiaogang Li
This experiment was carried out in Wheat Island Qingdao which is characterized with a typical industrial polluted marine atmosphere environment. The atmosphere contains a large amount of Cl− and SO2. The corrosion mechanism of printed circuit boards (PCBs) with an immersion silver surface finish (PCB-ImAg) in this phenomenon is still unknown. The corrosion behavior of PCB-ImAg is different under the influences of Cl− and SO2. Silver has strong resistance to Cl−, which mainly causes micro-hole corrosion. However, silver is sensitive to SO2. The corrosion degree can be accelerated in the environment containing Cl− and SO2. In this environment, the main corrosion products are oxides, sulfate and carbonate of silver and copper. The results summarized in this paper indicated that PCB-ImAg cannot be used in industrially polluted marine environment. Protective measures such as conformal coating are necessary to protect PCB-ImAg.
Graphical abstract
http://ift.tt/2fnZHj4
Direct preparation of low Ni-Cr alloy cast iron from red mud and laterite nickel ore
Publication date: 5 February 2017
Source:Materials & Design, Volume 115
Author(s): Aoping He, Jianmin Zeng
Based on the chemical composition requirements and enhancing the utilization value of the products, this work put forward a direct preparation method for low Ni-Cr alloy cast iron from red mud and laterite nickel ore by high-temperature carbothermal reduction smelting and refining. X-ray fluorescence (XRF), optical emission spectrometer (OES), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) attached with energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) analysis, hardness and polarization tests were used in the characterization process. The results show that low Ni-Cr alloy cast irons contain 1.50–2.00wt.% Ni and 0.70–0.80wt.% Cr have been prepared as the mass ratios of red mud to laterite nickel ore vary from 80:20 to 70:30, in which the recovery were 93.70% for Fe and 99.83% for Ni, respectively. The alloy cast iron was consisted of ledeburite and cementite matrix with evenly distributed Ni and Cr elements and block and flake graphite precipitated phase. With the increasing of Ni and Cr contents, the hardness and corrosion resistance of the alloy cast irons improved.
Graphical abstract
http://ift.tt/2fo0WP9
Overexpressed PLTP in macrophage may promote cholesterol accumulation by prolonged endoplasmic reticulum stress
Publication date: Available online 27 November 2016
Source:Medical Hypotheses
Author(s): Xinquan Yang, Yang Yu, Daxin Wang, Shucun Qin
It is well known that phospholipid transfer protein (PLTP) is involved in the lipid metabolism and development of atherosclerosis (AS). Abundant PLTP is considered to be expressed on the foam cells derived from monocyte/macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques, suggesting that high level of active PLTP may promote the formation of foam cells. However, the exact role of PLTP on the process of macrophage derived foam cell formation remains unclear. The accumulation of free cholesterol (FC) in the cytoplasm may lead to the prolonged endoplasmic reticulum stress(ERs) and the imbalance of intracellular cholesterol homeostasis. Different PLTP level definitely alternates the phospholipids(PL) and cholesterol level in plasma, strongly suggesting that active PLTP may change the level of FC and PL intracellularly, which subsequently induced the ERs in macrophage. Thus, we hypothesize that high level of PLTP may promote the accumulation of cholesterol in macrophage via the alteration ratio of FC to PL. Therefore, validating this hypothesis may clarify the role of PLTP in macrophage ERs in AS and also raise a novel strategy in the regression of AS plaques via restoring intracellular membrane lipid homeostasis and attenuating ERs.
http://ift.tt/2gz6uDM
Does Complement Factor H-Related protein 5 nephropathy (Troodos Nephropathy) protect from rickettsial infections?
Publication date: Available online 27 November 2016
Source:Medical Hypotheses
Author(s): Andreas Kousios
Complement Factor H-Related protein 5 Nephropathy (CFHR5N) is an endemic hereditary renal disease in the island of Cyprus. Although only very recently recognized, it has provided insight into previously unknown genetic aspects of complement-mediated renal diseases and in fact it has contributed to the introduction of the new disease classification, 'C3 Glomerulopathy'. Herein, based on evidence from epidemiological, genetic, clinical and basic research studies, the hypothesis that CFHR5N could be protective from rickettsial infections is proposed. Confirming this hypothesis, could have significant implications for the study of Complement Factor- H Related Proteins (CFHRs) in renal diseases and rickettsial molecular microbiology.
http://ift.tt/2gLU5zt
Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2023
(391)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (200)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (191)
-
►
2022
(2843)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (161)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (219)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (264)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (280)
-
►
2021
(5625)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (231)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (345)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (620)
-
►
2020
(2065)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (535)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (222)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (28)
-
►
2019
(9608)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (19)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (3791)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (3737)
-
►
2018
(69720)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (3507)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (3851)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (8116)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (7758)
-
►
2017
(111579)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (7718)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (7549)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (10753)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (10529)
-
▼
2016
(16402)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (7478)
-
▼
Νοεμβρίου
(1500)
-
▼
Νοε 27
(50)
- N-acetyl cysteine in the treatment of trichotillom...
- Combination treatment of propranolol, minocycline,...
- Reduction in psoriasis related pruritus during bio...
- Morphomechanics of dermis-A method for non-destruc...
- Erratum to: An experimental study on the compariso...
- Commentary on: “An update on peripheral ossifying ...
- Targeted inhibition of WRN helicase, replication s...
- Upregulated expression of Nucleostemin/GNL3 is ass...
- A novel lab-on-chip platform with integrated solid...
- Upconversion nanoparticles grafted molybdenum disu...
- Ag/N-doped reduced graphene oxide incorporated wit...
- Acknowledgement of reviewers 2015–16
- Society News
- Issue Information
- Corrigendum to “The effect of different drugs on t...
- New multi-functional infrared materials revealed
- Roll-process technology for flexible electronics
- Preparation, morphology and superior performances ...
- Hypoxia and HIF-1 activation in bacterial infections
- Kisspeptin expression is decreased in the arcuate ...
- Giving Tuesday: Show your support this Tuesday, No...
- Microsatellite polymorphism located immediately up...
- Triolein reduces MMP-1 upregulation in dermal fibr...
- Giving Tuesday: Show your support this Tuesday, No...
- Reevaluation of MAML2 fusion–negative mucoepidermo...
- Poorly cohesive cell (diffuse-infiltrative/signet ...
- Fenestration of auricular cartilage grafts to aid ...
- Repeated otalgia at mealtimes: osteochondroma of t...
- College student marijuana involvement: Perceptions...
- Combat experience and problem drinking in veterans...
- Psychiatric disorders, suicidal ideation, and sexu...
- AMP kinase promotes Bcl6 expression in both mouse ...
- Human amniotic epithelial cells inhibit CD4+ T cel...
- AMP kinase promotes Bcl6 expression in both mouse ...
- Human amniotic epithelial cells inhibit CD4+ T cel...
- Cost effective raspberry pi-based radio frequency ...
- The effects of inter-trial interval on implicit le...
- Scapular dyskinesis among competitive swimmers
- Does Ultrasound therapy add to the effects of exer...
- A Network Analysis of DSM-5 posttraumatic stress d...
- A novel silica nanowire-silica composite aerogels ...
- Printing of highly conductive carbon nanotubes fib...
- Investigation on induction brazing of revolving he...
- Enhanced multiscale modeling of macroscopic and mi...
- A new concept of universal substitutive explosive ...
- Compressive strength prediction of nano-silica inc...
- The corrosion behavior of PCB-ImAg in industry pol...
- Direct preparation of low Ni-Cr alloy cast iron fr...
- Overexpressed PLTP in macrophage may promote chole...
- Does Complement Factor H-Related protein 5 nephrop...
-
▼
Νοε 27
(50)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (900)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (1250)