Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2023
(391)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (200)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (191)
-
►
2022
(2843)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (161)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (219)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (264)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (280)
-
►
2021
(5625)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (231)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (345)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (620)
-
►
2020
(2065)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (535)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (222)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (28)
-
►
2019
(9608)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (19)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (3791)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (3737)
-
►
2018
(69720)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (3507)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (3851)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (8116)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (7758)
-
▼
2017
(111579)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (7718)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (7549)
-
▼
Απριλίου
(11636)
-
▼
Απρ 11
(422)
- Vision Loss, Rash, and Abnormal Brain Magnetic Res...
- Analyzing interactions on combining multiple clini...
- Two cases with an interseptal sinus cell mucocele:...
- One-lung ventilation using a bronchial blocker tub...
- Issue Information - Journal Info page
- Issue Information - TOC
- Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma with Cystic Cervical Meta...
- Subcutaneous Emphysema, Pneumomediastinum and Pneu...
- Tapia's Syndrome after Corrective Jaw Surgery unde...
- Extranodal NK/T Cell Lymphoma with Destruction of ...
- Report of Common Aeroallergens among Allergic Pati...
- Outcome of Incus Interposition after Preservation ...
- Otitis Media with Effusion in Children and the Imp...
- The Effect of Topical Tranexamic Acid on Bleeding ...
- Comparison of Temporalis Fascia and Full-Thickness...
- CYCORE: Cyberinfrastructure for Comparative Effect...
- Survey Study and Records Review of Treatment Outco...
- Anti-inflammatory, antimycobacterial and genotoxic...
- Anti-inflammatory activity of Crateva adansonii DC...
- CYCORE: Cyberinfrastructure for Comparative Effect...
- Survey Study and Records Review of Treatment Outco...
- Neue Therapieoption bei Acne vulgaris
- Narben effektiv behandeln
- Mit Nadeln gegen Narben
- Haartransplantation
- Neue Optionen der Teamarbeit in Kommunen
- Dermatokosmetika bei Akne: Was ist empfehlenswert?
- ADK aktiv bei dermatologischen Fortbildungen
- Tagung Dermatologische Praxis 2017
- Zytologie in der dermatologischen Praxis
- Mustervorlage für Hygieneplan
- Atopisches Ekzem: Proaktiv behandeln!
- Wasserlöslicher Nagellack
- Nicht invasives Lifting
- Inhaltsverzeichnis
- Die Adhärenz junger Akne-Patienten verbessern — ab...
- Pigmentverändungen vorbeugen
- Sterbegeld muss versteuert werden
- Lichttherapie gegen Juckreiz: UV-B nicht mit UV-A ...
- „Es klappt ja doch mit Familie!“
- „Ganzkörper-Lichttherapie oft zu früh abgesetzt“
- Stem cell delivery in tissue-specific hydrogel ena...
- Plasmonic titanium nitride nanoparticles for in vi...
- Vaccine nanocarriers: Coupling intracellular pathw...
- Local induction of lymphangiogenesis with engineer...
- Free Recall Test Experience Potentiates Strategy-D...
- Long-Term Memory Biases Auditory Spatial Attention.
- Abrupt Strategy Change Underlies Gradual Performan...
- Does Testing Increase Spontaneous Mediation in Lea...
- Novel thyroid hormone analogues, enzyme inhibitors...
- Nutritional approaches for managing obesity-associ...
- On “Cleft relapse and oronasal fistula after Furlo...
- “Rare place where I feel normal”: Perceptions of a...
- A randomized clinical trial about presence of path...
- Erratum to: Chronic hyperglycemia affects bone met...
- Contemporary surgical management of hypodontia
- New technique for midpalatal osteotomy in surgical...
- Bilateral submandibular rhabdomyomas: case report
- Surgeon-Reported Needs for Improved Training in Id...
- Reply
- Serum IgE as biomarker for predicting allergen imm...
- Novel Morpheme Learning in Monolingual and Bilingu...
- Calculus migration characterization during Ho:YAG ...
- Chirurgische Prävention hereditärer gastrointestin...
- Brain Activity During Phonation in Women With Musc...
- Temporal abundance and activity trends of vinyl ch...
- Phytotoxicity of CeO 2 nanoparticles on radish pla...
- The role of forest in mitigating the impact of atm...
- Enzyme-based solutions for textile processing and ...
- Revisiting inland hypoxia: diverse exceedances of ...
- Dysregulated homeostasis of target tissues or auto...
- Dysregulated homeostasis of target tissues or auto...
- Identification of a novel missence mutation in FGF...
- Mutation analysis of common GJB2, SCL26A4 and 12S ...
- Inverse relationship between toxic shock syndrome ...
- HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DQB1 Alleles in Chinese Han Patie...
- Pediatric sialolithiasis is not related to oral or...
- A fatal case of Gradenigo’s Syndrome in Zimbabwe a...
- Correlation of frontal sinus recess anatomy with e...
- Abrasion and blunt tissue trauma study of a novel ...
- Improving resident familiarity with the translabyr...
- Assessing cumulative acute toxicity of chemoradiot...
- Primary Extracranial Meningioma: A Rare Location
- Correlation of frontal sinus recess anatomy with e...
- Abrasion and blunt tissue trauma study of a novel ...
- Improving resident familiarity with the translabyr...
- Assessing cumulative acute toxicity of chemoradiot...
- Successful one-lung ventilation using a bronchial ...
- Clinical Thyroidology for the Public – Highlighted...
- Clinical Thyroidology for the Public – Highlighted...
- Phonological Process Occurrence in Typically Devel...
- CD11b regulates antibody class switching via induc...
- Positive feedback effect of PGE2 on cyclooxygenase...
- Lichtschutzfaktor 50+
- Dithranol
- Lichtschutz bei Xeroderma pigmentosum
- Erratum zu: Orale Schleimhautalteration – was ist ...
- Nasenmuschelchirurgie
- CD11b regulates antibody class switching via induc...
- Positive feedback effect of PGE2 on cyclooxygenase...
-
▼
Απρ 11
(422)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (10753)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (10529)
-
►
2016
(16402)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (7478)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (900)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (1250)
! # Ola via Alexandros G.Sfakianakis on Inoreader
Η λίστα ιστολογίων μου
Τρίτη 11 Απριλίου 2017
Analyzing interactions on combining multiple clinical guidelines
Source:Artificial Intelligence in Medicine
Author(s): Veruska Zamborlini, Marcos da Silveira, Cedric Pruski, Annette ten Teije, Edwin Geleijn, Marike van der Leeden, Martijn Stuiver, Frank van Harmelen
Accounting for patients with multiple health conditions is a complex task that requires analysing potential interactions among recommendations meant to address each condition. Although some approaches have been proposed to address this issue, important features still require more investigation, such as (re)usability and scalability. To this end, this paper presents an approach that relies on reusable rules for detecting interactions among recommendations coming from various guidelines. It extends a previously proposed knowledge representation model (TMR) to enhance the detection of interactions and it provides a systematic analysis of relevant interactions in the context of multimorbidity. The approach is evaluated in a case study on rehabilitation of breast cancer patients, developed in collaboration with experts. The results are considered promising to support the experts in this task.
http://ift.tt/2nD1G7q
Two cases with an interseptal sinus cell mucocele: The different mechanisms of the development varying in the time of the onset
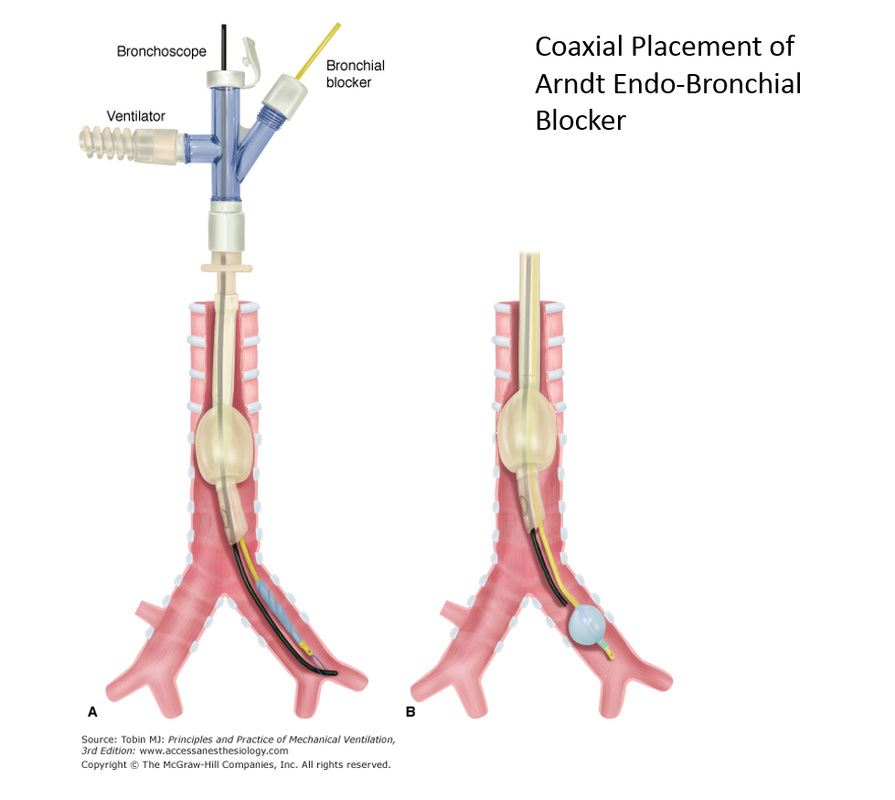
One-lung ventilation using a bronchial blocker tube for a large tracheal carcinoma resection
Anapafseos 5 . Agios Nikolaos
Crete.Greece.72100
2841026182
Issue Information - Journal Info page
No abstract is available for this article.
http://ift.tt/2o3hgog
Issue Information - TOC
No abstract is available for this article.
http://ift.tt/2orp4TV
Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma with Cystic Cervical Metastasis Masquerading as Branchial Cleft Cyst: A Potential Pitfall in Diagnosis and Management.
| Related Articles |
Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma with Cystic Cervical Metastasis Masquerading as Branchial Cleft Cyst: A Potential Pitfall in Diagnosis and Management.
Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;29(91):117-120
Authors: Sai-Guan L, Min-Han K, Kah-Wai N, Mohamad-Yunus MR
Abstract
INTRODUCTION: Most metastatic lymph nodes from head and neck malignancy are solid. Cystic nodes are found in 33% - 61% of carcinomas arise from Waldeyer's ring, of which only 1.8% - 8% originate are from the nasopharynx. Some cystic cervical metastases were initially presumed to be branchial cleft cyst. This case report aims to highlight the unusual presentation of cystic cervical metastasis secondary to nasopharyngeal carcinoma in a young adult. The histopathology, radiological features and management strategy were discussed.
CASE REPORT: A 36-year-old man presented with a solitary cystic cervical swelling, initially diagnosed as branchial cleft cyst. Fine needle aspiration yielded 18 ml of straw-coloured fluid. During cytological examination no atypical cells were observed. Computed tomography of the neck showed a heterogeneous mass with multiseptation medial to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Histopathological examination of the mass, post excision, revealed a metastatic lymph node. A suspicious mucosal lesion at the nasopharynx was detected after repeated thorough head and neck examinations and the biopsy result confirmed undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
CONCLUSION: Cystic cervical metastasis may occur in young patients under 40 years. The primary tumour may not be obvious during initial presentation because it mimicks benign branchial cleft cyst clinically. Retrospective review of the computed tomography images revealed features that were not characteristic of simple branchial cleft cyst. The inadequacy of assessment and interpretation had lead to the error in diagnosis and subsequent management. Metastatic head and neck lesion must be considered in a young adult with a cystic neck mass.
PMID: 28393061 [PubMed - in process]
http://ift.tt/2nA3E8F
Subcutaneous Emphysema, Pneumomediastinum and Pneumothorax in a Patient with Dermatomyositis.
| Related Articles |
Subcutaneous Emphysema, Pneumomediastinum and Pneumothorax in a Patient with Dermatomyositis.
Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;29(91):113-116
Authors: Bakhshaee M, Jokar MH, Mirfeizi Z, Atabati E, Tarighat S
Abstract
INTRODUCTION: Spontaneous pneumomediastinum, pneumothorax, and subcutaneous emphysema are rare, but serious complications of inflammatory myopathies and occur more commonly in DM than PM. complications of dermatomyositis (DM) and polymyositis (PM), both of which can be fatal.
CASE REPORT: A 20-year-old woman was admitted with neck pain, dyspnea, cough, and fever. She had been diagnosed with dermatomyositis 21 months prior. A thorax computed tomography (CT) scan revealed ground glass opacities in her lungs, pneumomediastinum, pneumothorax, and subcutaneous emphysema. Despite intensive immunosuppressive therapy, clinical deterioration and radiological progression were observed, ultimately the patient died.
CONCLUSION: During the care for a patient with dermatomyositis, the otorhinolaryngologist should be cautious of rapidly progressive and fatal neck subcutaneous emphysema. For a patient with dermatomyositis and with normal bronchoscopy and esophagoscopy, the main treatment is control of dermatomyositis with medical therapy. Therefore, a tracheostomy and/or mechanical ventilation may not be necessary.
PMID: 28393060 [PubMed - in process]
http://ift.tt/2p3PMDy
Tapia's Syndrome after Corrective Jaw Surgery under General Anesthesia: A Case Report.
| Related Articles |
Tapia's Syndrome after Corrective Jaw Surgery under General Anesthesia: A Case Report.
Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;29(91):109-111
Authors: Izadi F, Ahmadi A, Daneshvar A, Safdarian M
Abstract
INTRODUCTION: Tapia's syndrome is a rare complication of recurrent laryngeal and hypoglossal nerve paralysis due to anesthetic airway mismanagement or malpositioning of the patient's head during surgery.
CASE REPORT: Here we present a case of Tapia's syndrome in a 22-year-old male after corrective jaw surgery under general anesthesia, with a long period of recovery, related to airway management procedures and/or overstretching of the neck during positioning for surgery.
CONCLUSION: Although it is a rare condition, every surgeon should be aware of Tapia's syndrome in order to consider the correct positioning of the head and endotracheal tube during surgery and avoid this complication.
PMID: 28393059 [PubMed - in process]
http://ift.tt/2nA3qyg
Extranodal NK/T Cell Lymphoma with Destruction of the Uvulae: A Case Report.
| Related Articles |
Extranodal NK/T Cell Lymphoma with Destruction of the Uvulae: A Case Report.
Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;29(91):101-108
Authors: Jabbari Azad F, Delavarian Z, Hatami M, Rahimi H, Abdolvahed MR
Abstract
INTRODUCTION: Extranodal Natural Killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma (NKTCL) nasal type is a rare but well-known disease with poor prognosis. NKTCL is more prevalent in Asia and comprises about 7-10% of all non-Hodgkin lymphoma cases in this region. The characteristic clinical pattern of NKTCL is the destruction of the midline structures of the mid-face.
CASE REPORT: The present study examines a case of NKTCL in a 23-year-old man with a destructive ulcer of the palate and uvulae. Based on immunohistochemical results, after three months of delay, the definitive diagnosis was revealed to be Extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma. Following the third cycle of chemotherapy, the patient died due to sepsis and infection.
CONCLUSION: It is very common to misdiagnose NKTCL with other clinical conditions such as necrotizing stomatitis, deep fungal ulcers, Wegener's Granulomatosis disease, etc. Delay in diagnosis can worsen the course of the disease and its prognosis.
PMID: 28393058 [PubMed - in process]
http://ift.tt/2olUWYH
Report of Common Aeroallergens among Allergic Patients in Northeastern Iran.
| Related Articles |
Report of Common Aeroallergens among Allergic Patients in Northeastern Iran.
Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;29(91):89-94
Authors: Mahboubi Oskouei Y, Farid Hosseini R, Ahanchian H, Jarahi L, Ariaee N, Jabbari Azad F
Abstract
INTRODUCTION: The prevalence of atopic diseases has increased in recent decades dramatically. The most common aeroallergens in Northeastern Iran have not been fully defined. Determining the most common aeroallergens in allergic patients based on the skin prick test (SPT) was aimed in this investigation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: This cross-sectional study enrolled 1,006 allergic patients (aged 1-86 years) from October 2010 to February 2014 referred to the Allergy clinics of Mashhad University of Medical Science. After completing a checklist including demographic information, the SPT was performed according to the patients' history of aeroallergen sensitivity.
RESULTS: Patients with symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, and urticaria were enrolled. Ninety seven percent of patients had a positive skin test to at least one aeroallergen. The most prevalent allergens were Russian thistle (Salsola kali) (50.2%), ash (Fraxinus excelsior) (36.7%), grass mix (29.1%), tree mix (21.6%), and pigweed mix (19.5%). Common allergens in patients with different symptoms of allergic disorders were as follows: asthma (Russian thistle, grass mix, ash, tree mix, and Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus); allergic rhinitis (Russian thistle, ash, grass mix, tree mix, and pigweed mix); urticaria (Russian thistle, ash, grass mix, pigweed mix, and tree mix) and atopic dermatitis (Russian thistle, grass mix, ash, tree mix, and pigweed mix). In the spring, the most prevalent allergens were Russian thistle, ash, grass mix, tree mix, and pigweed mix. In the summer, Russian thistle, ash, grass mix, tree mix, and pigweed mix accounted for the most prevalent allergens. During the autumn, Russian thistle, ash, grass mix, pigweed mix and lamb's quarter were the most common aeroallergens, while in the winter, Russian thistle, ash, grass mix, pigweed mix, and tree mix were shown to be the most common aeroallergens.
CONCLUSION: Determination of the most common aeroallergens in this area is unavoidable in the diagnosis and management of allergic disorders. Understanding the prevalence of the most common aeroallergens such as Russian thistle in 50.2% of people or other common aeroallergens can help patients and specialists to more easily identify suspected allergens, reduce costs, and support immunotherapy of allergic patients in this area. Moreover, it is helpful in avoiding pollens or cross-reactions.
PMID: 28393056 [PubMed - in process]
http://ift.tt/2p3UXmU
Outcome of Incus Interposition after Preservation in Soft Tissue.
| Related Articles |
Outcome of Incus Interposition after Preservation in Soft Tissue.
Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;29(91):83-88
Authors: Faramarzi M, Roosta S, Dianat M
Abstract
INTRODUCTION: The lenticular process of the incus succumbs to necrosis in chronic otitis media. Few researchers have addressed the issue of autograft incus preservation in the soft tissue of the tragus or mastoid cavity. Nonetheless, preservation of the incus in this method during the second stage of ossiculoplasty is a subject that is still up for debate. This study was carried out to demonstrate the hearing outcome after a modification of the incus interposition technique, which involved preserving it in the periauricular soft tissue.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: In the primary operations, tympanoplasty was performed with a postauricular incision. At the end of the surgery, a small pocket was created to preserve the incus beneath the temporalis fascia. The second stage of ossiculoplasty was performed 6 to 18 months after the primary operation. Post-operative pure tone audiometry was analyzed after at least 12 months and was considered successful after achieving an air-bone gap (ABG) within 20 dB.
RESULTS: In this paper, we analyzed 199 ears. The mean duration of follow up was 2.5 years. We achieved post-operative ABG within 20 dB in 157 patients (78.9% of patients).
CONCLUSION: This study indicates the efficacy and safety of incus interposition when it is preserved in the postauricular soft tissue.
PMID: 28393055 [PubMed - in process]
http://ift.tt/2p3XbCt
Otitis Media with Effusion in Children and the Impact of Risk Factors on Serum Cytokine Levels.
| Related Articles |
Otitis Media with Effusion in Children and the Impact of Risk Factors on Serum Cytokine Levels.
Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;29(91):75-81
Authors: Arshi S, Dehghani Firouzabadi F, Ghalehbaghi B, Dehghani Firouzabadi A, Jalali F, Shekarabi M, Sirous R, Dehghani Firouzabadi M
Abstract
INTRODUCTION: To evaluate the role of allergic-type and infectious-type cytokines in children with chronic otitis media with effusion (OME).
MATERIALS AND METHODS: We investigated serum levels of interleukins (IL)-4, IL-5, and IL-13, along with interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in 35 children with OME and 28 healthy controls.
RESULTS: Children with OME had significantly higher levels of IL-5 in comparison with the control group, ranging from 1 pg/ml in cases to 0.04 pg/ml in controls (P=0.009). However, after adjusting for confounding variables, there was no significant difference in serum levels of IL-13, IL-4, IFN-γ, or TNF-α between the two groups (P=0.287, P=0.627, P=0.793, and P=0.217, respectively).
CONCLUSIONS: The findings of this study suggest that in comparison with the control group, serum IL-5 levels were elevated in OME cases.
PMID: 28393054 [PubMed - in process]
http://ift.tt/2nAbzT6
The Effect of Topical Tranexamic Acid on Bleeding Reduction during Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery.
| Related Articles |
The Effect of Topical Tranexamic Acid on Bleeding Reduction during Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery.
Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;29(91):69-74
Authors: Baradaranfar MH, Dadgarnia MH, Mahmoudi H, Behniafard N, Atighechi S, Zand V, Baradaranfar A, Vaziribozorg S
Abstract
INTRODUCTION: Bleeding is a common concern during functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) that can increase the risk of damage to adjacent vital elements by reducing the surgeon's field of view. This study aimed to explore the efficacy of topical tranexamic acid in reducing intraoperative bleeding.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: This double-blind, randomized clinical trial was conducted in 60 patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with polyposis (CRSwP) who underwent FESS. Patients were randomly divided into two groups; tranexamic or saline treatment. During surgery, normal saline (400 mL) or tranexamic acid (2 g) in normal saline with a total volume of 400 mL were used in the saline and tranexamic groups, respectively, for irrigation and suctioning. The surgeons' assessment of field of view during surgery and intraoperative blood loss were recorded.
RESULTS: Mean blood loss was 254.13 mL in the saline group and 235.6 mL in the tranexamic group (P=0.31). No statistically significant differences between the two groups were found in terms of other investigated variables, such as surgical field quality based on Boezzart's scale (P=0.30), surgeon satisfaction based on a Likert scale (P=0.54), or duration of surgery (P=0.22).
CONCLUSION: Use of tranexamic acid (2 g in 400 mL normal saline) through washing of the nasal mucosa during FESS did not significantly reduce blood loss or improve the surgical field of view. Further studies with larger sample sizes and higher drug concentrations, and using other methods of administration, such as spraying or applying pledgets soaked in tranexamic acid, are recommended.
PMID: 28393053 [PubMed - in process]
http://ift.tt/2nYSyoZ
Comparison of Temporalis Fascia and Full-Thickness Cartilage Palisades in Type-I Underlay Tympanoplasty for Large/Subtotal Perforations.
| Related Articles |
Comparison of Temporalis Fascia and Full-Thickness Cartilage Palisades in Type-I Underlay Tympanoplasty for Large/Subtotal Perforations.
Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;29(91):63-68
Authors: Pradhan P, Anant A, Venkatachalam VP
Abstract
INTRODUCTION: To demonstrate surgical techniques and to compare the anatomical and functional outcomes between temporalis fascia and cartilage palisade grafting in type-I underlay tympanoplasty in patients with large/subtotal perforation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Temporalis fascia and cartilage palisade grafting were conducted in Group A and Group B, respectively, each containing 30 patients with large/subtotal perforations. Pure tone audiogram (PTA) and speech reception thresholds (SRT) were performed preoperatively and at each postoperative visit; i.e. at the end of Month 1,3,6, and 24. A 10-dB closure of air bone gap (ABG) and a 10-dB improvement in SRT were considered significant.
RESULTS: The graft uptake rates were 80% and 96.7% in Group A and Group B, respectively, at the end of 24 months. In total, 90% of Group A and 88% in Group B had significant improvement in hearing (ABG ≥10 dB). The mean improvement in SRT in the fascia and cartilage groups was 10 dB and 9 dB, respectively. Seventy-five percent of patients in Group A and 60% of patients in Group B had a significant gain in SRT.
CONCLUSION: Although both temporalis fascia and cartilage palisades can effectively be used for tympanic membrane (TM) grafting in difficult perforations, the latter is considered to be the better autograft, not only because of superior graft uptake but also because it results in a comparable hearing outcome.
PMID: 28393052 [PubMed - in process]
http://ift.tt/2p3ZghM
CYCORE: Cyberinfrastructure for Comparative Effectiveness Research - Feasibility Trial
Interventions: Device: Smart phone; Device: Accelerometers; Device: Blood Pressure Monitor; Other: Telephone Surveys; Other: Home Visit; Device: Home Health Hub and Modem; Device: Carbon Monoxide (CO) Monitor; Device: Heat Rate Monitor; Device: Global Positioning System (GPS) Device; Other: Surveys; Device: Weight Scale; Device: Fitbit Monitor; Behavioral: At-Home Exercise Program; Behavioral: Physical Fitness Tests; Behavioral: Questionnaires; Behavioral: Lean Body Mass Assessment
Sponsors: M.D. Anderson Cancer Center; National Cancer Institute (NCI)
Recruiting - verified April 2017
http://ift.tt/2onubDi
Survey Study and Records Review of Treatment Outcomes in Freeman-Sheldon Syndrome
Interventions: Other: PTSD Checklist-Civilian (PCL-C); Other: Modified Flanagan Quality of Life Scale; Other: Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D); Other: Functional Enquiry (or Review of Systems) Form; Other: Study of Therapeutic Outcomes and Practices in Freeman-Sheldon Syndrome (STOP-FSS) Questionnaire; Other: FSRG Semi-Structured Quality of Life Interview (FSRG SSQLI); Other: Medical Records Review
Sponsor: Freeman-Sheldon Research Group, Inc.
Recruiting - verified April 2017
http://ift.tt/2oxDSRE
Anti-inflammatory, antimycobacterial and genotoxic evaluation of Doliocarpus dentatus
Publication date: 23 May 2017
Source:Journal of Ethnopharmacology, Volume 204
Author(s): Raissa Borges Ishikawa, Maicon Matos Leitão, Roberto Mikio Kassuya, Luis Fernando Macorini, Flora Martinez Figueira Moreira, Claudia Andrea Lima Cardoso, Roberta Gomes Coelho, Arnildo Pott, Guilherme Martins Gelfuso, Julio Croda, Rodrigo Juliano Oliveira, Candida Aparecida Leite Kassuya
Ethnopharmacological relevanceDoliocarpus dentatus is a medicinal plant widely used in Mato Grosso do Sul State for removing the swelling pain caused by the inflammation process and for treating urine retention.Aim of the studyThe genotoxic aspects and the anti-inflammatory and antimycobacterial activity of the ethanolic extract obtained from the leaves of D. dentatus (EEDd) were investigated.Materials and methodsThe EEDd was evaluated against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and the compound composition was evaluated and identified by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The mice received oral administration of EEDd (30–300mg/kg) in carrageenan models of inflammation, and EEDd (10–1000mg/kg) was assayed by the comet, micronucleus, and phagocytosis tests and by the peripheral leukocyte count.ResultsPhenols (204.04mg/g), flavonoids (89.17mg/g), and tannins (12.05mg/g) as well as sitosterol-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, kaempferol 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside, betulinic acid and betulin were present in the EEDd. The value of minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of EEDd was 62.5µg/mL. The EEDd induced a significant decrease in the edema, mechanical hypersensitivity and leukocyte migration induced by carrageenan. The comet and micronucleus tests indicated that the EEDd was not genotoxic. The EEDd also did not change the phagocytic activity or the leukocyte perLipheral count.ConclusionsThe EEDd does not display genotoxicity, phagocytosis and could act as an antimycobacterial and anti-inflammatory agent. This study should contribute to ensuring the safe use of EEDd.
Graphical abstract
http://ift.tt/2nD4FfV
Anti-inflammatory activity of Crateva adansonii DC on keratinocytes infected by Staphylococcus aureus: From traditional practice to scientific approach using HPTLC-densitometry
Publication date: 23 May 2017
Source:Journal of Ethnopharmacology, Volume 204
Author(s): Kplolali Ahama-Esseh, Charles Bodet, Akossiwa Quashie-Mensah-Attoh, Magali Garcia, Isabelle Théry-Koné, Joelle Dorat, Comlan De Souza, Cécile Enguehard-Gueiffier, Leslie Boudesocque-Delaye
Ethnopharmacoligical relevanceLeaves of Crateva adansonii DC (Capparidaceae), a small bush found in Togo, are widely used in traditional medicine to cure infectious abscesses. Traditional healers of Lomé harvest only budding leaves early in the morning, in specific area in order to prepare their drugs.Aim of the studyThe main goal was to validate the ancestral picking practices, and to assess the activity of C. adansonii medicine towards infectious abscesses.Materials and methodsA phytochemical screening of various C. adansonii leaf samples was performed using an original HPTLC-densitometry protocol and major flavonoids were identified and quantified. C. adansonii samples were collected in different neighborhoods of Lomé, at different harvesting-times and at different ages. Radical scavenging capacity, using DPPH assay, was used to quickly screen all extracts. Extracts were tested for anti-Staphylococcus aureus activity and anti-inflammatory effect on human primary keratinocytes infected by S. aureus. IL6, IL8 and TNFα expression and production were assessed by RT-PCR and ELISA assays.ResultsUsing antioxidant activity as selection criteria, optimal extracts were obtained with budding leaves, collected at 5:00am in Djidjolé neighborhood. This extract showed the strongest anti-inflammatory effect on S. aureus-infected keratinocytes by reducing IL6, IL8 and TNFα expression and production. None of the extracts inhibited the growth of S. aureus.ConclusionsThose results validate the traditional practices and the potential of C. adansonii as anti-inflammatory drug. Our findings suggest that traditional healers should add to C. adansonii leaves an antibacterial plant of Togo Pharmacopeia, in order to improve abscess healing.
Graphical abstract
http://ift.tt/2nCR2xn
CYCORE: Cyberinfrastructure for Comparative Effectiveness Research - Feasibility Trial
Interventions: Device: Smart phone; Device: Accelerometers; Device: Blood Pressure Monitor; Other: Telephone Surveys; Other: Home Visit; Device: Home Health Hub and Modem; Device: Carbon Monoxide (CO) Monitor; Device: Heat Rate Monitor; Device: Global Positioning System (GPS) Device; Other: Surveys; Device: Weight Scale; Device: Fitbit Monitor; Behavioral: At-Home Exercise Program; Behavioral: Physical Fitness Tests; Behavioral: Questionnaires; Behavioral: Lean Body Mass Assessment
Sponsors: M.D. Anderson Cancer Center; National Cancer Institute (NCI)
Recruiting - verified April 2017
http://ift.tt/2onubDi
Survey Study and Records Review of Treatment Outcomes in Freeman-Sheldon Syndrome
Interventions: Other: PTSD Checklist-Civilian (PCL-C); Other: Modified Flanagan Quality of Life Scale; Other: Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D); Other: Functional Enquiry (or Review of Systems) Form; Other: Study of Therapeutic Outcomes and Practices in Freeman-Sheldon Syndrome (STOP-FSS) Questionnaire; Other: FSRG Semi-Structured Quality of Life Interview (FSRG SSQLI); Other: Medical Records Review
Sponsor: Freeman-Sheldon Research Group, Inc.
Recruiting - verified April 2017
http://ift.tt/2oxDSRE
Neue Optionen der Teamarbeit in Kommunen
Eine Versorgung chronisch Kranker über alle Sektoren und Betreuungsbereiche hinweg ist in Deutschland meist noch Utopie. Doch mancherorts gibt es Keimzellen für neue Modelle mit Vorbildcharakter.
http://ift.tt/2prWVtz
Tagung Dermatologische Praxis 2017
Bei der Dermatologischen Praxis in Frankenthal konnten die Teilnehmer wieder aus einer Vielzahl an unterschiedlichen Veranstaltungen mit über 70 Referenten auswählen. Ein Schwerpunkt war am Samstag die Behandlung der Akne. Ebenfalls am Samstag hatten die Besucher auch Gelegenheit, sich in einem Workshop der Arbeitsgemeinschaft Ästhetische Dermatologie und Kosmetologie (ADK) aus erster Hand über wichtige Themen der ästhetischen Medizin zu informieren.
http://ift.tt/2orhAQR
Lichttherapie gegen Juckreiz: UV-B nicht mit UV-A kombinieren!
Bei Patienten mit Psoriasis oder atopischem Ekzem bringt es für den Juckreiz offenbar nichts, eine Phototherapie mit UV-B-Strahlen durch einen UV-A-Anteil zu ergänzen. Angesichts möglicher kumulativer Nebenwirkungen empfehlen Schweizer Forscher, die Indikation für den UV-A-Zusatz restriktiv zu stellen.
http://ift.tt/2prQ3wC
„Es klappt ja doch mit Familie!“
Beruf und Familie — das funktioniert auch in eigener Praxis. Vielleicht sogar besser als im Krankenhaus. Diese Erkenntnis konnten junge Ärzte vom „Tag der Chancen" in Thüringen im März mitnehmen.
http://ift.tt/2or4aEC
Stem cell delivery in tissue-specific hydrogel enabled meniscal repair in an orthotopic rat model
Source:Biomaterials, Volume 132
Author(s): Xiaoning Yuan, Yiyong Wei, Aránzazu Villasante, Johnathan J.D. Ng, Derya E. Arkonac, Pen-hsiu Grace Chao, Gordana Vunjak-Novakovic
Interest in non-invasive injectable therapies has rapidly risen due to their excellent safety profile and ease of use in clinical settings. Injectable hydrogels can be derived from the extracellular matrix (ECM) of specific tissues to provide a biomimetic environment for cell delivery and enable seamless regeneration of tissue defects. We investigated the in situ delivery of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) in decellularized meniscus ECM hydrogel to a meniscal defect in a nude rat model. First, decellularized meniscus ECM hydrogel retained tissue-specific proteoglycans and collagens, and significantly upregulated expression of fibrochondrogenic markers by hMSCs versus collagen hydrogel alone in vitro. The meniscus ECM hydrogel in turn supported delivery of hMSCs for integrative repair of a full-thickness defect model in meniscal explants after in vitro culture and in vivo subcutaneous implantation. When applied to an orthotopic model of meniscal injury in nude rat, hMSCs in meniscus ECM hydrogel were retained out to eight weeks post-injection, contributing to tissue regeneration and protection from joint space narrowing, pathologic mineralization, and osteoarthritis development, as evidenced by macroscopic and microscopic image analysis. Based on these findings, we propose the use of tissue-specific meniscus ECM-derived hydrogel for the delivery of therapeutic hMSCs to treat meniscal injury.
http://ift.tt/2ooobf5
Plasmonic titanium nitride nanoparticles for in vivo photoacoustic tomography imaging and photothermal cancer therapy
Source:Biomaterials, Volume 132
Author(s): Wenya He, Kelong Ai, Chunhuan Jiang, Yuanyuan Li, Xiangfu Song, Lehui Lu
Titanium nitride, an alternative plasmonic material to gold with unique physiochemical properties, has been widely used in microelectronics, biomedical devices and food-contact applications. However, its potential application in the area of biomedicine has not been effectively explored. With the spectral match of their plasmon resonance band and the biological transparency window as well as good biocompatibility, titanium nitride nanoparticles (TiN NPs) are promising photoabsorbing agents for photothermal therapy (PTT) and photoacoustic imaging. Nevertheless, the photothermal performance of TiN NPs has not been investigated until now. Here, we presented the investigation of employing TiN NPs as photoabsorbing agents for in vivo photoacoustic tomography (PAT) imaging-guided photothermal cancer therapy. Our experimental results showed that TiN NPs could strongly absorb the NIR light and provided up to 48% photothermal conversion efficiency. After PEGylation, the resultant nanoparticles demonstrated improved physiological stability and extensive blood retention. Following intravenously administration, they could simultaneously enhance the photoacoustic signals of the tumor region and destroy tumors in the tumor-bearing mouse model by taking advantage of the photothermal effect of the TiN NPs. Our findings highlighted the great potential of plasmonic TiN NPs in detection and treatment of cancer.
http://ift.tt/2o0eTlN
Vaccine nanocarriers: Coupling intracellular pathways and cellular biodistribution to control CD4 vs CD8 T cell responses
Source:Biomaterials, Volume 132
Author(s): Marcela Rincon-Restrepo, Aaron Mayer, Sylvie Hauert, Daniel K. Bonner, Edward A. Phelps, Jeffrey A. Hubbell, Melody A. Swartz, Sachiko Hirosue
Nanoparticle delivery systems are known to enhance the immune response to soluble antigens (Ags) and are thus a promising tool for the development of new vaccines. Our laboratory has engineered two different nanoparticulate systems in which Ag is either encapsulated within the core of polymersomes (PSs) or decorated onto the surface of nanoparticles (NPs). Previous studies showed that PSs are better at enhancing CD4 T cells and antibody titers, while NPs preferentially augment cytotoxic CD8 T cells. Herein, we demonstrate that the differential activation of T cell immunity reflects differences in the modes of intracellular trafficking and distinct biodistribution of the Ag in lymphoid organs, which are both driven by the properties of each nanocarrier. Furthermore, we found that Ags within PSs promoted better CD4 T cell activation and induced a higher frequency of CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells. These differences correlated with changes in the frequency of germinal center B cells and plasma cell formation, which reflects the previously observed antibody titers. Our results show that PSs are a promising vector for the delivery of Ags for B cell vaccine development. This study demonstrates that nanocarrier design has a large impact on the quality of the induced adaptive immune response.
http://ift.tt/2oomfmF
Local induction of lymphangiogenesis with engineered fibrin-binding VEGF-C promotes wound healing by increasing immune cell trafficking and matrix remodeling
Publication date: July 2017
Source:Biomaterials, Volume 131
Author(s): Esra Güç, Priscilla S. Briquez, Didier Foretay, Manuel A. Fankhauser, Jeffrey A. Hubbell, Witold W. Kilarski, Melody A. Swartz
Lymphangiogenesis occurs in inflammation and wound healing, yet its functional roles in these processes are not fully understood. Consequently, clinically relevant strategies for therapeutic lymphangiogenesis remain underdeveloped, particularly using growth factors. To achieve controlled, local capillary lymphangiogenesis with protein engineering and determine its effects on fluid clearance, leukocyte trafficking, and wound healing, we developed a fibrin-binding variant of vascular endothelial growth factor C (FB-VEGF-C) that is slowly released upon demand from infiltrating cells. Using a novel wound healing model, we show that implanted fibrin containing FB-VEGF-C, but not free VEGF-C, could stimulate local lymphangiogenesis in a dose-dependent manner. Importantly, the effects of FB-VEGF-C were restricted to lymphatic capillaries, with no apparent changes to blood vessels and downstream collecting vessels. Leukocyte intravasation and trafficking to lymph nodes were increased in hyperplastic lymphatics, while fluid clearance was maintained at physiological levels. In diabetic wounds, FB-VEGF-C-induced lymphangiogenesis increased extracellular matrix deposition and granulation tissue thickening, indicators of improved wound healing. Together, these results indicate that FB-VEGF-C is a promising strategy for inducing lymphangiogenesis locally, and that such lymphangiogenesis can promote wound healing by enhancing leukocyte trafficking without affecting downstream lymphatic collecting vessels.
http://ift.tt/2o0dXy0
Free Recall Test Experience Potentiates Strategy-Driven Effects of Value on Memory.
http://ift.tt/2o2Rctd
Long-Term Memory Biases Auditory Spatial Attention.
http://ift.tt/2p3RW66
Abrupt Strategy Change Underlies Gradual Performance Change: Bayesian Hierarchical Models of Component and Aggregate Strategy Use.
http://ift.tt/2o2W1Tt
Does Testing Increase Spontaneous Mediation in Learning Semantically Related Paired Associates?.
http://ift.tt/2p3VrJx
Novel thyroid hormone analogues, enzyme inhibitors and mimetics, and their action
Publication date: Available online 11 April 2017
Source:Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology
Author(s): Santanu Mondal, Govindasamy Mugesh
Thyroid hormones (THs) play key roles in modulating the overall metabolism of the body, protein synthesis, fat metabolism, neuronal and bone growth, and cardiovascular as well as renal functions. In this review, we discuss on the thyroid hormone synthesis and activation, thyroid hormone receptors (TRs) and mechanism of action, applications of thyroid hormone analogues, particularly the compounds that are selective ligands for TRβ receptors, or enzyme inhibitors for the treatment of thyroidal disorders with a specific focus on thyroid peroxidase and iodothyronine deiodinases. We also discuss on the development of small-molecule deiodinase mimetics and their mechanism of deiodination, as these compounds have the potential to regulate the thyroid hormone levels.
Graphical abstract
http://ift.tt/2o2KtiX
Nutritional approaches for managing obesity-associated metabolic diseases
Obesity is an ongoing pandemic and serves as a causal factor of a wide spectrum of metabolic diseases including diabetes, fatty liver disease, and cardiovascular disease. Much evidence has demonstrated that nutrient overload initiates or exacerbates inflammatory responses in tissues/organs involved in the regulation of systemic metabolic homeostasis. This obesity-associated inflammation is usually at a low-grade and viewed as metabolic inflammation. When it exists continuously, inflammation inappropriately alters metabolic pathways and impairs insulin signaling cascades in peripheral tissues/organs such as adipose tissue, the liver and skeletal muscle, resulting in local fat deposition and insulin resistance and systemic metabolic dysregulation. In addition, inflammatory mediators, e.g., proinflammatory cytokines, and excessive nutrients, e.g., glucose and fatty acids, act together to aggravate local insulin resistance and form a vicious cycle to further disturb local metabolic pathways and exacerbate systemic metabolic dysregulation. Owing to the critical role of nutrient metabolism in the control of the initiation and progression of inflammation and insulin resistance, nutritional approaches have been implicated as effective ways for managing obesity and obesity-associated metabolic diseases. Based on the mounting evidence generated from both basic and clinical research, nutritional approaches are commonly used for suppressing inflammation, improving insulin sensitivity, and/or decreasing fat deposition. Consequently, the combined effects are responsible for improvement of systemic insulin sensitivity and metabolic homeostasis.
http://ift.tt/2onD0ge
On “Cleft relapse and oronasal fistula after Furlow palatoplasty in infants with cleft palate: incidence and risk factors” by Li et al.
I read with great interest the study by Li et al. entitled "Cleft relapse and oronasal fistula after Furlow palatoplasty in infants with cleft palate: incidence and risk factors"1. The aim of the study was to investigate the risk factors for the development of postoperative cleft relapse and oronasal fistula after Furlow palatoplasty. By using multivariate analysis, they showed that only the width of the cleft had a statistically significant impact on the incidence of cleft relapse and oronasal fistula.
http://ift.tt/2oqt9Yy
“Rare place where I feel normal”: Perceptions of a social support conference among parents of and people with Moebius syndrome
Source:Research in Developmental Disabilities, Volume 64
Author(s): Kathleen R. Bogart, Erika Frandrup, Taylor Locke, Hanna Thompson, Natalie Weber, Jacqueline Yates, Nicholas Zike, Amanda R. Hemmesch Breaker
BackgroundMoebius syndrome is a rare congenital disorder resulting in impaired facial and eye movement. People with rare diseases like Moebius syndrome experience stigma and a lack of specialized information. Support conferences may provide important forms of social support for people with rare disorders.AimsTo examine reasons for attending, benefits, and limitations of support conferences.Methods and procedures50 adults with Moebius syndrome and 57 parents of people with Moebius syndrome completed open-ended items in an online study.Outcomes and resultsMixed- methods content analysis revealed that companionship and informational support were most frequently mentioned as reasons for and benefits of attending. Finances were the most frequently mentioned reason for not attending. Parents were more likely than people with Moebius to describe instrumental support as a conference benefit. When describing conference limitations, parents were significantly more concerned by lack of information relevance, while people with Moebius noted more often that conference attributes were not relevant to their age.Conclusions and implicationsBeing surrounded by others who share one's condition offers a unique opportunity for destigmatizing companionship support, which normalizes, reduces isolation, and promotes solidarity. Ways to increase facilitators and decrease barriers to accessing support for rare disorders should be investigated.
http://ift.tt/2p3AfU4
A randomized clinical trial about presence of pathogenic micro-flora and risk of peri-implantitis: comparison of two different types of implant-abutment connections
OBJECTIVE: The aim of this in vivo study was to evaluate two different types of implant-abutment connections: screwed connection and cemented connection, analyzing peri-implant bacteria microflora as well as other clinical parameters.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Twenty implants were selected, inserted in 20 patients, 10 with a screwed implant-abutment connection (Group 1) and 10 with a cemented implant-abutment connection (Group 2). The peri-implant microflora was collected, after at least 360 days from the prosthetic rehabilitation, using paper points inserted in peri-implant sulcus for 30 s. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) Real-time analyzed the presence of 9 bacteria periodontal-pathogens and Candida albicans.
RESULTS: Our findings showed that bacteria colonized all Groups analyzed, the average bacterial count was 3.7 E +08 (±1.19) in Group 1, compared to 2.1 E +08 (±0.16) in Group 2; no statistically significant differences were observed (p>0.0.5). In Group 1, however, bacterial colonization of peri-implant sulci was over the pathogenic threshold for 5 bacteria, indicating a high-risk of peri-implantitis. Also in Group 2, results showed a microflora composed by all bacteria analyzed but, in this case, bacterial colonization of peri-implant sulci was over the pathogenic threshold for only 1 bacterium, indicating a lower risk of peri-implantitis. Moreover, clinical parameters (PPD > 3 mm and m SBI > 0) confirmed a greater risk of peri-implantitis in Group 1 compared to Group 2 (p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS: We concluded that, also after only 360 days, implants with screwed connection showed a higher risk of peri-implantitis that implants with cemented connection.
L'articolo A randomized clinical trial about presence of pathogenic micro-flora and risk of peri-implantitis: comparison of two different types of implant-abutment connections sembra essere il primo su European Review.
http://ift.tt/2o0KuUN
Contemporary surgical management of hypodontia
Hypodontia is the term most commonly applied to the condition in which teeth congenitally fail to develop. Such cases differ from teeth that have been lost early or that have failed to erupt, although their initial presentation may be similar and therefore not recognised. The range of missing teeth and their physical and psychological results is large, and the difference in complexity in the management of a patient with isolated hypodontia compared with one with oligodontia or anodontia together with skeletal and orthognathic discrepancies should not be underestimated.
http://ift.tt/2o2Jr6r
New technique for midpalatal osteotomy in surgically-assisted rapid palatal expansion
Surgically-assisted rapid palatal expansion is an acceptable approach for the correction of a transverse deficiency of the maxilla in skeletally mature patients (Fig. 1). Although it is effective, there may be serious complications,1 such as the loss of periodontal bone and the central incisors,2 but preoperative orthodontic preparation minimises the risk. Separation of the roots of the central incisors by preoperative orthodontic management improves overall clinical success, but the risk of dental complications still exists.
http://ift.tt/2oqyK11
Bilateral submandibular rhabdomyomas: case report
Rhabdomyoma is a benign tumour of striated muscle, and outside the heart they are rare and classified as adult, fetal, and genital subtypes.1 They are found twice as often in men as women, and commonly in adults over 40 years old.2 Of the 115 reported cases of extracardiac rhabdomyoma, 76% were found in the head and neck, but rarely in the submandibular space.3 We describe an exceptional example of bilateral rhabdomyomas in the submandibular spaces.
http://ift.tt/2prmEmf
Surgeon-Reported Needs for Improved Training in Identifying and Managing Free Flap Compromise
J reconstr Microsurg
DOI: 10.1055/s-0037-1601423
Background This study examined the need for improved training in the identification and management of free flap (FF) compromise and assessed a potential role for simulated scenario training. Methods Online needs assessment surveys were completed by plastic surgeons and a subsample with expertise in microsurgery education participated in focus groups. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and mixed qualitative methods. Results In this study, 77 surgeons completed surveys and 11 experts participated in one of two focus groups. Forty-nine (64%) participants were educators, 65 and 45% of which reported having an insufficient volume of FF cases to adequately teach the management and identification of compromise, respectively. Forty-three percent of educators felt that graduating residents are not adequately prepared to manage FF compromise independently. Exposure to normal and abnormal FF cases was felt to be critical for effective training by focus group participants. Experts identified low failure rates, communication issues, and challenging teaching conditions as current barriers to training. Most educators (74%) felt that simulated scenario training would be "very useful" or "extremely useful" to current residents. Focus groups highlighted the need for a widely accepted algorithm for re-exploration and salvage on which to base the development of a training adjunct consisting of simulated scenarios. Conclusion Trainee exposure to FF compromise is inadequate in existing plastic surgery programs. Early exposure, high case volume, and a standardized algorithmic approach to management with a focus on decision making may improve training. Simulated scenario training may be valuable in addressing current barriers.
[...]
Thieme Medical Publishers 333 Seventh Avenue, New York, NY 10001, USA
Article in Thieme eJournals:
Table of contents | Abstract | Full text
http://ift.tt/2oqBlrJ
Reply
I thank Giorgio Ciprandi1 for commenting on my recent article2 and for proposing, on the basis of results of reports cited in his letter, that serum levels of allergen-specific IgE (sIgE) could be considered a potential biomarker to identify those patients with allergic rhinitis most likely to respond to allergen-specific immunotherapy (SIT). Specifically, Ciprandi highlighted articles reporting that subjects with allergic rhinitis whose blood sIgE level exceeded specified amounts were much more likely to respond to SIT than those with lower levels of sIgE; he also cited 1 article reporting conflicting results.
http://ift.tt/2o4vW7d
Serum IgE as biomarker for predicting allergen immunotherapy effectiveness
Galli1 recently provided an interesting review concerning precision medicine in allergy. He stated that, to his knowledge, no predictive tests have yet been shown to have clinical utility in predicting responses of individual patients to allergen immunotherapy (AIT). In addition, to underline the relevance of this issue, he cited Akdis and Akdis2 who noted that the general use of disease endotypes for allergies and asthma and correct selection of the responder patient population with defined biomarkers remain essential unmet needs in the clinical setting.
http://ift.tt/2oVWfAr
Novel Morpheme Learning in Monolingual and Bilingual Children
http://ift.tt/2prfluz
Calculus migration characterization during Ho:YAG laser lithotripsy by high-speed camera using suspended pendulum method
Abstract
Calculus migration is a common problem during ureteroscopic laser lithotripsy procedure to treat urolithiasis. A conventional experimental method to characterize calculus migration utilized a hosting container (e.g., a "V" grove or a test tube). These methods, however, demonstrated large variation and poor detectability, possibly attributed to the friction between the calculus and the container on which the calculus was situated. In this study, calculus migration was investigated using a pendulum model suspended underwater to eliminate the aforementioned friction. A high-speed camera was used to study the movement of the calculus which covered zero order (displacement), first order (speed), and second order (acceleration). A commercialized, pulsed Ho:YAG laser at 2.1 μm, a 365-μm core diameter fiber, and a calculus phantom (Plaster of Paris, 10 × 10 × 10 mm3) was utilized to mimic laser lithotripsy procedure. The phantom was hung on a stainless steel bar and irradiated by the laser at 0.5, 1.0, and 1.5 J energy per pulse at 10 Hz for 1 s (i.e., 5, 10, and 15 W). Movement of the phantom was recorded by a high-speed camera with a frame rate of 10,000 FPS. The video data files are analyzed by MATLAB program by processing each image frame and obtaining position data of the calculus. With a sample size of 10, the maximum displacement was 1.25 ± 0.10, 3.01 ± 0.52, and 4.37 ± 0.58 mm for 0.5, 1, and 1.5 J energy per pulse, respectively. Using the same laser power, the conventional method showed <0.5 mm total displacement. When reducing the phantom size to 5 × 5 × 5 mm3 (one eighth in volume), the displacement was very inconsistent. The results suggested that using the pendulum model to eliminate the friction improved sensitivity and repeatability of the experiment. A detailed investigation on calculus movement and other causes of experimental variation will be conducted as a future study.
http://ift.tt/2ox86E3
Chirurgische Prävention hereditärer gastrointestinaler Tumordispositionen
Zusammenfassung
Hintergrund
Tumorerkrankungen stellen die zweithäufigste Todesursache in der industrialisierten Welt dar. Das zunehmende Verständnis der molekularen Ätiopathogenese von Tumoren und des Einflusses auf die klinische Heterogenität und das Therapieansprechen hat zu einer Präzisierung onkologischer Strategien geführt. Hereditäre Dispositionssyndrome werden aufgrund fehlender Awareness hierzulande nur zu einem kleinen Anteil durch klinische und konsekutive molekulargenetische Testung identifiziert. In Anbetracht des weitreichenden Benefits für Betroffene und deren Familien wären systematische molekulargenetische Untersuchungen bei allen gastrointestinalen Tumoren sinnvoll.
Methode
Eine Recherche und Auswertung aktueller Literatur wurden durchgeführt.
Ergebnisse und Schlussfolgerungen
Durch Identifikation von Mutationsträgern eröffnen sich zahlreiche Optionen für Präventionsstrategien. Diese reichen von einer Änderung der Lifestyle-Faktoren über eine medikamentöse Prävention bis hin zu risikoreduzierenden prophylaktischen Operationen. Allerdings muss hierbei das syndrombezogene Risiko des Auftretens der Tumorerkrankung (Penetranz) unter Berücksichtigung des Gens oder evtl. des genauen Genlokus und des Geschlechts (Gender) sowie des Alters mit der Morbidität jeder Maßnahme genau abgewogen werden. Es ist die Rolle der Behandler unterschiedlicher Disziplinen, über die Möglichkeiten und Grenzen präventiver Maßnahmen so zu beraten, dass Betroffene eine informierte Entscheidung treffen können. In dieser Übersichtsarbeit werden der aktuelle Stand präventiver Optionen in der Behandlung hereditärer Tumorerkrankungen des Gastrointestinaltrakts dargestellt und Konsequenzen für das klinische Management diskutiert.
http://ift.tt/2o1uCkT
Brain Activity During Phonation in Women With Muscle Tension Dysphonia: An fMRI Study
The main objectives of this functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study are (1) to investigate brain activity during phonation in women with muscle tension dysphonia (MTD) in comparison with healthy controls; and (2) to explain the neurophysiological mechanism of laryngeal hyperfunction/tension during phonation in patients with MTD.
http://ift.tt/2p5y2EP
Temporal abundance and activity trends of vinyl chloride (VC)-degrading bacteria in a dilute VC plume at Naval Air Station Oceana
Abstract
Assessment and monitoring of microbial community dynamics is useful when tracking the progress of vinyl chloride (VC) bioremediation strategies, particularly in dilute plumes where apparent VC attenuation rates are low. In a long-term field study, the abundance and the activity of microbial VC degraders were tracked in three monitoring wells (MW05, MW25, and MW19) along a dilute VC plume at Naval Air Station (NAS) Oceana. High-throughput sequencing of partial 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes and transcripts revealed diverse groundwater microbial communities and showed that methanotrophs and anaerobic respirers (e.g., methanogens, sulfate reducers, and iron reducers) were among the most active and abundant guilds. Quantitative PCR analysis showed that among bacterial guilds with a potential to contribute to VC biodegradation, methanotrophs were the most abundant and active microbial group. Ethene-oxidizing bacterial populations were less abundant and relatively inactive compared to methanotrophs. In MW19, expression of functional genes associated with both aerobic VC oxidation and anaerobic VC reduction was observed. Overall, our results reveal that the groundwater community contains various active bacterial guilds previously associated with metabolic and cometabolic VC degradation processes either under aerobic and anaerobic conditions that might have contributed to the slowly decreasing VC concentrations at the NAS Oceana site over the 6-year study period.
http://ift.tt/2ox2pq0
Phytotoxicity of CeO 2 nanoparticles on radish plant ( Raphanus sativus )
Abstract
Cerium oxide nanoparticles (CeO2 NPs) have been considered as one type of emerging contaminants that pose great potential risks to the environment and human health. The effect of CeO2 NPs on plant-edible parts and health evaluation remains is necessary and urgently to be developed. In this study, we cultivated radish in Sigma CeO2 NP (<25 nm)-amended soils across a series of concentration treatments, i.e., 0 mg/kg as the control and 10, 50, and 100 mg/kg CeO2 NPs. The results showed that CeO2 NPs accelerated the fresh biomass accumulation of radish plant; especially in the treatment of 50 mg/kg CeO2 NPs, root expansion was increased by 2.2 times as much as the control. In addition, the relative chlorophyll content enhanced by 12.5, 12.9, and 12.2% was compared to control on 40 cultivation days. CeO2 NPs were mainly absorbed by the root and improved the activity of antioxidant enzyme system to scavenge the damage of free radicals in radish root and leaf. In addition, this study also indicated that the nanoparticles might enter the food chain through the soil into the edible part of the plant, which will be a potential threat to human health.
http://ift.tt/2p5kl8G
The role of forest in mitigating the impact of atmospheric dust pollution in a mixed landscape
Abstract
Atmospheric dust pollution, especially particulate matter below 2.5 μm, causes 3.3 million premature deaths per year worldwide. Although pollution sources are increasingly well known, the role of ecosystems in mitigating their impact is still poorly known. Our objective was to investigate the role of forests located in the surrounding of industrial and urban areas in reducing atmospheric dust pollution. This was tested using lichen transplants as biomonitors in a Mediterranean regional area with high levels of dry deposition. After a multivariate analysis, we have modeled the maximum pollution load expected for each site taking into consideration nearby pollutant sources. The difference between maximum expected pollution load and the observed values was explained by the deposition in nearby forests. Both the dust pollution and the ameliorating effect of forested areas were then mapped. The results showed that forest located nearby pollution sources plays an important role in reducing atmospheric dust pollution, highlighting their importance in the provision of the ecosystem service of air purification.
http://ift.tt/2ox8L8G
Enzyme-based solutions for textile processing and dye contaminant biodegradation—a review
Abstract
The textile industry, as recognized conformist and stake industry in the world's economy, is facing serious environmental challenges. In numerous industries, in practice, various chemical-based processes from initial sizing to final washing are fascinating harsh environment concerns. Some of these chemicals are corrosive to equipment and cause serious damage itself. Therefore, in the twenty-first century, chemical and allied industries quest a paradigm transition from traditional chemical-based concepts to a greener, sustainable, and environmentally friendlier catalytic alternative, both at the laboratory and industrial scales. Bio-based catalysis offers numerous benefits in the context of biotechnological industry and environmental applications. In recent years, bio-based processing has received particular interest among the scientist for inter- and multi-disciplinary investigations in the areas of natural and engineering sciences for the application in biotechnology sector at large and textile industries in particular. Different enzymatic processes such as chemical substitution have been developed or in the process of development for various textile wet processes. In this context, the present review article summarizes current developments and highlights those areas where environment-friendly enzymatic textile processing might play an increasingly important role in the textile industry. In the first part of the review, a special focus has been given to a comparative discussion of the chemical-based "classical/conventional" treatments and the modern enzyme-based treatment processes. Some relevant information is also reported to identify the major research gaps to be worked out in future.
http://ift.tt/2p5y2oj
Revisiting inland hypoxia: diverse exceedances of dissolved oxygen thresholds for freshwater aquatic life
Abstract
Water resources in many regions are stressed by impairments resulting from climate change, population growth and urbanization. In the United States (US), water quality criteria (WQC) and standards (WQS) were established to protect surface waters and associated designated uses, including aquatic life. In inland waters of the south central US, for example, depressed dissolved oxygen (DO) consistently results in impaired aquatic systems due to noncompliance with DO WQC and WQS. In the present study, we systematically examined currently available DO threshold data for freshwater fish and invertebrates and performed probabilistic aquatic hazard assessments with low DO toxicity data that were used to derive the US Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) Ambient Water Quality Criteria (AWQC) for DO and newly published information. Aquatic hazard assessments predicted acute invertebrate DO thresholds for Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera, or Trichoptera (EPT) taxa and species inhabiting lotic systems to be more sensitive than fish. For example, these organisms were predicted to have acute low DO toxicity thresholds exceeding the US EPA guidelines 17, 26, 31 and 38% and 13, 24, 30 and 39% of the time at 8.0, 5.0, 4.0 and 3.0 mg DO/L, respectively. Based on our analysis, it appears possible that low DO effects to freshwater organisms have been underestimated. We also identified influences of temperature on low DO thresholds and pronounced differences in implementation and assessment of the US EPA AWQC among habitats, seasons, and geographic regions. These results suggest some implemented DO guidelines may adversely affect the survival, growth, and reproduction of freshwater aquatic organisms in a region susceptible to climate change and rapid population growth. Given the global decline of species, particularly invertebrates, low DO threshold information, including sublethal (e.g., reproduction, behavior) responses, for additional species (e.g., mollusks, other invertebrates, warm water fish) across seasons, habitats, and life history stages using consistent experimental designs is needed to support more sustainable environmental assessment efforts and management of biodiversity protection goals in inland waters.
http://ift.tt/2owVsF8
Dysregulated homeostasis of target tissues or autoantigens - a novel principle in autoimmunity
Source:Autoimmunity Reviews
Author(s): Frank Petersen, Xiaoyang Yue, Gabriela Riemekasten, Xinhua Yu
Monogenic autoimmune disorders provide a powerful tool for our understanding of the principles of autoimmunity due to the obvious impact of a single gene on the disease. So far, approximately 100 single gene defects causing murine monogenic autoimmune disorders have been reported and the functional characterization of these genes will provide significant progress in understanding the nature of autoimmunity. According to their function, genes leading to monogenic autoimmune disorders can be categorized into two groups. An expectable first group contains genes involved in the homeostasis of the immune system, including homeostasis of immune organs and immune cells. Intriguingly, the second group consists of genes functionally involved in the homeostasis of target tissues or autoantigens. According to our novel hypothesis, we propose that autoimmunity represents a consequence of a dysregulated homeostasis of the immune system and/or its targets including autoantigens and target tissues. In this review we refer to both aspects of homeostasis in autoimmunity with a highlight on the role of the homeostasis of target tissues and antoantigens.
http://ift.tt/2owSD70
Dysregulated homeostasis of target tissues or autoantigens - a novel principle in autoimmunity
Source:Autoimmunity Reviews
Author(s): Frank Petersen, Xiaoyang Yue, Gabriela Riemekasten, Xinhua Yu
Monogenic autoimmune disorders provide a powerful tool for our understanding of the principles of autoimmunity due to the obvious impact of a single gene on the disease. So far, approximately 100 single gene defects causing murine monogenic autoimmune disorders have been reported and the functional characterization of these genes will provide significant progress in understanding the nature of autoimmunity. According to their function, genes leading to monogenic autoimmune disorders can be categorized into two groups. An expectable first group contains genes involved in the homeostasis of the immune system, including homeostasis of immune organs and immune cells. Intriguingly, the second group consists of genes functionally involved in the homeostasis of target tissues or autoantigens. According to our novel hypothesis, we propose that autoimmunity represents a consequence of a dysregulated homeostasis of the immune system and/or its targets including autoantigens and target tissues. In this review we refer to both aspects of homeostasis in autoimmunity with a highlight on the role of the homeostasis of target tissues and antoantigens.
http://ift.tt/2owSD70
Identification of a novel missence mutation in FGFR3 gene in an Iranian family with LADD syndrome by Next-Generation Sequencing
Lacrimo-auriculo-dento-digital syndrome (LADD) is a multiple congenital anomaly and a genetically heterogeneous disorder. The aim of this study was to identify the pathogenic gene in an Iranian family with LADD syndrome and review the literature on reported mutations that involved in pathogenesis of LADD syndrome. One novel variant, c.1882 G>A, in fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) was identified by next generation sequencing and Sanger sequencing. The heterozygous FGFR3 c.1882 G>A variant results in substitution of aspartic acid with asparagine at amino acid 628 (p.D628N) and co-segregated with the phenotype in the LADD family.
http://ift.tt/2pr7GfN
Mutation analysis of common GJB2, SCL26A4 and 12S rRNA genes among 380 deafness patients in northern China
The molecular etiology of nonsyndromic deafness in Chinese population has not been investigated systematically, our study is aim to investigate the molecular etiology of nonsyndromic deafness patients from Northern China (Heilongjiang province), in order to provide genetic test and counseling to families.
http://ift.tt/2nCk2oR
Inverse relationship between toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 antibodies and interferon-γ and interleukin-6 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with pediatric tonsillitis caused by Staphylococcus aureus
Pediatric tonsillitis is frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus, which is the most common pathogen that causes serious pyogenic infections in humans and endangers human health. S. aureus produces numerous potent virulence factors that play a critical role in the pathogenesis of the infection caused by this bacterium, and one of the most important toxins produced by S. aureus is toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1). The aim of this study is to investigate the first time the levels of IFN-γ and interleukin IL-6 in TSST-1-stimulated PBMCs from pediatric tonsillitis patients and the correlation of these cytokine levels with TSST-1-specific IgG in serum.
http://ift.tt/2pruH2o
HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DQB1 Alleles in Chinese Han Patients with Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis
Juvenile-Onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (JORRP) is a rare benign neoplasm of the respiratory mucosa caused by human papilloma virus. Previous studies on the possible associations between HLA alleles and JORRP have shown various results in different ethnic groups. The present study aims to investigate the association between JORRP and HLA class II DRB1and DQB1 alleles in Chinese Han children. We found that the frequencies of HLA-DRB1*03:01 (pc = 0.0378, OR = 4.8) and HLA-DQB1*02:01 (pc = 0.021, OR = 4.8) alleles were significantly higher in patients with JORRP than in controls.
http://ift.tt/2nCqsV0
Pediatric sialolithiasis is not related to oral or oropharyngeal infection: A population-based case control study using the Korean National Health Insurance Database
Poor oral hygiene is one of the risk factors for sialolithiasis particularly in adults; however the etiology of sialolithiasis in pediatric patients remains largely unknown. The purpose of this study is to identify the association between sialolithiasis and the oral/oropharyngeal infections in the pediatric population, as surrogate indicators for oral hygiene and retrograde infections to the affected salivary gland.
http://ift.tt/2prlyGL
A fatal case of Gradenigo’s Syndrome in Zimbabwe and the Danish-Zimbabwean ENT collaboration
As a part of a bilateral educational exchange program two Danish ENT residents were invited to Zimbabwe in 2015. During this exchange a 9-year-old girl was admitted due to complications to acute otitis media (AOM). She developed Gradenigo's syndrome and later on a brain abscess leading to a fatal outcome. Life threatening complications to AOM are rare in developed countries today but are still a challenge in developing countries. We put forward this case from a developing country to bring focus to the fact that a fatal outcome is the consequence if specialist treatment is not accessible.
http://ift.tt/2nCjgbz
Correlation of frontal sinus recess anatomy with ethnicity, gender, and pathology
Research on frontal sinus cells has been conflicting regarding relationship between frontal sinus cells and frontal sinus disease. There are no published studies regarding gender differences in frontal sinus disease. No comparisons between African Americans and Caucasians and frontal sinus disease have been published. This study attempts to define the above relationships as well as the relationship between number and types of cells and disease.
http://ift.tt/2nCq4WA
Abrasion and blunt tissue trauma study of a novel flexible robotic system in the porcine model
The objective of this study was to determine if a flexible robotic system caused increased tissue reaction when accessing the oropharynx and hypopharynx compared to intubation controls in only 2 scenarios: high speed tissue impact and multiple unit insertions and retractions. The data obtained were submitted as part of the entirety of information submitted for FDA approval.
http://ift.tt/2o2kp7z
Improving resident familiarity with the translabyrinthine approach to the internal auditory canal
To increase otolaryngology resident experience with drilling and dissection of the internal auditory canal (IAC) via a translabyrinthine approach.
http://ift.tt/2nClV4U
Assessing cumulative acute toxicity of chemoradiotherapy in head and neck cancer with or without induction chemotherapy
To compare cumulative acute toxicity in head and neck cancer patients treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy alone (CCRT) versus induction chemotherapy (IC) followed by CCRT (I/CCRT).
http://ift.tt/2o2qbWK
Primary Extracranial Meningioma: A Rare Location
Abstract
Meningiomas are benign extraaxial tumors of the central nervous system (CNS). Extracranial meningiomas are extremely rare (2%) and can develop as a direct extension from a primary intracranial meningioma or as true primary extracranial meningioma originating from ectopic arachnoid cells. Only eight cases of primary meningioma in the jaw have been reported to date. Extracranial meningiomas are frequently misdiagnosed, resulting in inappropriate clinical management. The aim of this article was to describe the case of a man with an asymptomatic swelling in the right retromolar area over a period of 2 months. Cone beam computed tomography was performed to determine the extension and involvement of the adjacent structures. Histopathological findings and immunohistochemical analysis aided in the diagnosis of primary extracranial meningioma in the mandible and several aspects of this unusual neoplasm are reviewed. The treatment of choice was a partial resection of the mandible and reconstruction with autogenous iliac tricortical bone. Five years after surgery, the patient remains free of disease.
http://ift.tt/2p41Emb
Correlation of frontal sinus recess anatomy with ethnicity, gender, and pathology
Research on frontal sinus cells has been conflicting regarding relationship between frontal sinus cells and frontal sinus disease. There are no published studies regarding gender differences in frontal sinus disease. No comparisons between African Americans and Caucasians and frontal sinus disease have been published. This study attempts to define the above relationships as well as the relationship between number and types of cells and disease.
http://ift.tt/2nCq4WA
Abrasion and blunt tissue trauma study of a novel flexible robotic system in the porcine model
The objective of this study was to determine if a flexible robotic system caused increased tissue reaction when accessing the oropharynx and hypopharynx compared to intubation controls in only 2 scenarios: high speed tissue impact and multiple unit insertions and retractions. The data obtained were submitted as part of the entirety of information submitted for FDA approval.
http://ift.tt/2o2kp7z
Improving resident familiarity with the translabyrinthine approach to the internal auditory canal
To increase otolaryngology resident experience with drilling and dissection of the internal auditory canal (IAC) via a translabyrinthine approach.
http://ift.tt/2nClV4U
Assessing cumulative acute toxicity of chemoradiotherapy in head and neck cancer with or without induction chemotherapy
To compare cumulative acute toxicity in head and neck cancer patients treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy alone (CCRT) versus induction chemotherapy (IC) followed by CCRT (I/CCRT).
http://ift.tt/2o2qbWK
Successful one-lung ventilation using a bronchial blocker tube for a large tracheal carcinoma resection
The informed consent was obtained from the patient. A 57-year old woman was diagnosed as a trachea adenoid cystic carcinoma. A large tumor was found in the upper tracheal under fiber bronchoscopy (FBO), which the lower edge of the tumor was about 3cm proximal to the carina and the tumor size was about 4cm, obstructing the tracheal lumen by 92%. The gap at the narrowest intraluminal point was about 0.5cm (Fig.1A, B). Abnormal FEV 1% FVC: 22.07 and PaO2: 6.5kPa were detected by pulmonary function test and arterial blood gas test on room air respectively.
http://ift.tt/2owUhWj
Clinical Thyroidology for the Public – Highlighted Article
From Clinical Thyroidology for the Public: Hyperthyroidism, or an overactive thyroid, is a common disorder with an estimated lifetime risk of 2-5% in the general population. Read More….
The post Clinical Thyroidology for the Public – Highlighted Article appeared first on American Thyroid Association.
http://ift.tt/2nBV355
Clinical Thyroidology for the Public – Highlighted Article
From Clinical Thyroidology for the Public: Hyperthyroidism, or an overactive thyroid, is a common disorder with an estimated lifetime risk of 2-5% in the general population. Read More….
The post Clinical Thyroidology for the Public – Highlighted Article appeared first on American Thyroid Association.
http://ift.tt/2nBV355
Phonological Process Occurrence in Typically Developing Toddlers
Folia Phoniatr Logop 2016;68:199-204
http://ift.tt/2p4X7j0
CD11b regulates antibody class switching via induction of AID
Source:Molecular Immunology, Volume 87
Author(s): Seohyun Park, Hyunsub Sim, Hye-In Kim, Daecheol Jeong, Guang Wu, Soo Young Cho, Young Seek Lee, Hyung-Joo Kwon, Keunwook Lee
The integrin CD11b, which is encoded by the integrin subunit alpha M (ITGAM), is primarily expressed on the surface of innate immune cells. Genetic variations in ITGAM are among the strongest risk factors for systemic lupus erythematosus, an autoimmune disease characterized by the presence of autoantibodies. However, the regulatory function of CD11b in the antibody responses remains unclear. Here, we report the induction of CD11b in activated B2 B cells and define its unexpected role in immunoglobulin heavy chain class switch recombination (CSR). LPS-activated B cells lacking CD11b yielded fewer IgG subtypes such as IgG1 and IgG2a in vitro, and immunization-dependent CSR and affinity maturation of antibodies were severely impaired in CD11b-deficient mice. Notably, we observed the reduced expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), an enzyme that initiates CSR and somatic hypermutation, and ectopic expression of AID was sufficient to rescue the defective CSR of CD11b-deficient B cells. LPS-induced phosphorylation of NF-κB p65 and IκBα was attenuated in CD11b-deficient B cells, and hyperactivation of IκB kinase 2 restored the defective AID expression and CSR, which implied that CD11b regulates the NF-κB-dependent induction of AID. Overall, our experimental evidence emphasized the function of CD11b in antibody responses and the role of CD11b as a vital regulator of CSR.
http://ift.tt/2oVLs9G
Positive feedback effect of PGE2 on cyclooxygenase-2 expression is mediated by inhibition of Akt phosphorylation in human follicular dendritic cell-like cells
Source:Molecular Immunology, Volume 87
Author(s): Jongseon Choe, Yongdae Yoon, Jini Kim, Yu-Jin Jung
Prostaglandins (PGs) are bioactive lipid mediators generated from the phospholipids of cell membrane in response to various inflammatory signals. To understand the potential role of PGs in PG production itself during immune inflammatory responses, we examined the effect of PGE2, PGF2α, and beraprost on COX-2 expression using follicular dendritic cell (FDC)-like HK cells isolated from human tonsils. Those three PGs specifically augmented COX-2 protein expression in a dose-dependent manner after 4 or 8h of treatment. The enhancing effect was also reflected in the actual production of PGs and the viable cell recovery of germinal center B-cells. To investigate the underlying molecular mechanism, we examined the impact of PI3K inhibitors on PG-induced COX-2 expression. Interestingly, COX-2 induction by PGE2 and beraprost, but not PGF2α, was enhanced by wortmannin and LY294002. In line with this result, Akt phosphorylation was inhibited by PGE2 and beraprost but not by PGF2α. The distinct effect of PGE2 and beraprost from PGF2α was reproduced in Akt-knockdowned HK cells. Our current findings imply that PGE2 and PGI2 stimulate COX-2 expression in FDC by inhibiting Akt phosphorylation. Additional studies are warranted to determine the potential role of Akt as a therapeutic target in patients with inflammatory disorders.
http://ift.tt/2o4hVqa
Lichtschutzfaktor 50+
Zusammenfassung
Der Nutzen von Sonnenschutzmitteln mit Lichtschutzfaktoren (LSF) jenseits 50 ist umstritten. Um eine Irreführung des Konsumenten zu vermeiden, sind mehrere Länder bereits dazu übergegangen, LSF über 50 nicht mehr auf Sonnenschutzmitteln zu deklarieren. Argumente gegen hohe LSF sind das Risiko eines unausgewogenen Schutzes, der die Gefahr von Schäden durch längerwellige ultraviolette Strahlung erhöhen könnte; Vermittlung eines falschen Sicherheitsgefühls, das zur zeitlichen Ausdehnung der Sonnenexposition verleiten könnte; gesundheitliche Risiken durch höhere Konzentration an Filtersubstanzen und die nur marginal höhere Lichtblockade. Demgegenüber steht die Erkenntnis, dass der funktionelle LSF von Sonnenschutzmitteln in der praktischen Anwendung ohnehin weit hinter dem deklarierten LSF zurückbleibt und daher der Einsatz von höheren LSF bei sensitiven Individuen und starker UV-Belastung durchaus Sinn machen könnte.
http://ift.tt/2o23FNZ
Dithranol
http://ift.tt/2o22gH6
Lichtschutz bei Xeroderma pigmentosum
Zusammenfassung
Xeroderma pigmentosum ist eine seltene autosomal-rezessiv vererbte Genodermatose, die durch Mutationen in Genen, verantwortlich für die Reparatur UV-induzierter DNA-Schäden, verursacht wird. Die Erkrankung ist charakterisiert durch erhöhte UV-Lichtsensitivität und eine Poikilodermie, Augenbeteiligung und bei manchen Patienten durch ausgeprägte Sonnenbrände und neurologische Mitbeteiligung. Es besteht ein erhöhtes Risiko für die Entwicklung von Augen- und Hauttumoren an sonnenexponierten Arealen. Derzeit besteht keine kurative Therapie. Als protektive Maßnahme wird ein absoluter Lichtschutz vor allen UV-Strahlungen dringend empfohlen.
http://ift.tt/2p3d9wJ
Nasenmuschelchirurgie
Zusammenfassung
Die Nase bildet die ersten 8 cm des oberen Respirationstrakts und dient neben der Luftzufuhr der Reinigung, Befeuchtung und Temperierung der Atemluft. Dies wird als Konditionierung bezeichnet. Diffusor und Beschleuniger der Atemluft ist die Nasenklappenregion, gebildet aus dem Kopf der unteren Nasenmuschel, Anteilen des knorpeligen Septums und des Lateralknorpels. Voraussetzungen sind regelrechte mukoziliäre Clearance und ausreichender Luftdurchtritt. Die Hypertrophie der unteren Nasenmuscheln ist eine der häufigsten Ursachen symptomatischer Nasenatmungsbehinderungen. Rhinometrische Verfahren stellen bei unklaren Fällen die erweiterte Diagnostik dar. Neben der konservativen Therapie einer allergischen oder vasomotorischen Rhinitis mittels spezifischer Immuntherapie bzw. topischer Kortikoide gibt es diverse interventionelle Verfahren zur Verkleinerung des Muschelgewebes bei einem hohen Maß an Schonung der respiratorischen Schleimhaut.
http://ift.tt/2p57iUQ
CD11b regulates antibody class switching via induction of AID
Source:Molecular Immunology, Volume 87
Author(s): Seohyun Park, Hyunsub Sim, Hye-In Kim, Daecheol Jeong, Guang Wu, Soo Young Cho, Young Seek Lee, Hyung-Joo Kwon, Keunwook Lee
The integrin CD11b, which is encoded by the integrin subunit alpha M (ITGAM), is primarily expressed on the surface of innate immune cells. Genetic variations in ITGAM are among the strongest risk factors for systemic lupus erythematosus, an autoimmune disease characterized by the presence of autoantibodies. However, the regulatory function of CD11b in the antibody responses remains unclear. Here, we report the induction of CD11b in activated B2 B cells and define its unexpected role in immunoglobulin heavy chain class switch recombination (CSR). LPS-activated B cells lacking CD11b yielded fewer IgG subtypes such as IgG1 and IgG2a in vitro, and immunization-dependent CSR and affinity maturation of antibodies were severely impaired in CD11b-deficient mice. Notably, we observed the reduced expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), an enzyme that initiates CSR and somatic hypermutation, and ectopic expression of AID was sufficient to rescue the defective CSR of CD11b-deficient B cells. LPS-induced phosphorylation of NF-κB p65 and IκBα was attenuated in CD11b-deficient B cells, and hyperactivation of IκB kinase 2 restored the defective AID expression and CSR, which implied that CD11b regulates the NF-κB-dependent induction of AID. Overall, our experimental evidence emphasized the function of CD11b in antibody responses and the role of CD11b as a vital regulator of CSR.
http://ift.tt/2oVLs9G
Positive feedback effect of PGE2 on cyclooxygenase-2 expression is mediated by inhibition of Akt phosphorylation in human follicular dendritic cell-like cells
Source:Molecular Immunology, Volume 87
Author(s): Jongseon Choe, Yongdae Yoon, Jini Kim, Yu-Jin Jung
Prostaglandins (PGs) are bioactive lipid mediators generated from the phospholipids of cell membrane in response to various inflammatory signals. To understand the potential role of PGs in PG production itself during immune inflammatory responses, we examined the effect of PGE2, PGF2α, and beraprost on COX-2 expression using follicular dendritic cell (FDC)-like HK cells isolated from human tonsils. Those three PGs specifically augmented COX-2 protein expression in a dose-dependent manner after 4 or 8h of treatment. The enhancing effect was also reflected in the actual production of PGs and the viable cell recovery of germinal center B-cells. To investigate the underlying molecular mechanism, we examined the impact of PI3K inhibitors on PG-induced COX-2 expression. Interestingly, COX-2 induction by PGE2 and beraprost, but not PGF2α, was enhanced by wortmannin and LY294002. In line with this result, Akt phosphorylation was inhibited by PGE2 and beraprost but not by PGF2α. The distinct effect of PGE2 and beraprost from PGF2α was reproduced in Akt-knockdowned HK cells. Our current findings imply that PGE2 and PGI2 stimulate COX-2 expression in FDC by inhibiting Akt phosphorylation. Additional studies are warranted to determine the potential role of Akt as a therapeutic target in patients with inflammatory disorders.
http://ift.tt/2o4hVqa
Nasenmuschelchirurgie
Zusammenfassung
Die Nase bildet die ersten 8 cm des oberen Respirationstrakts und dient neben der Luftzufuhr der Reinigung, Befeuchtung und Temperierung der Atemluft. Dies wird als Konditionierung bezeichnet. Diffusor und Beschleuniger der Atemluft ist die Nasenklappenregion, gebildet aus dem Kopf der unteren Nasenmuschel, Anteilen des knorpeligen Septums und des Lateralknorpels. Voraussetzungen sind regelrechte mukoziliäre Clearance und ausreichender Luftdurchtritt. Die Hypertrophie der unteren Nasenmuscheln ist eine der häufigsten Ursachen symptomatischer Nasenatmungsbehinderungen. Rhinometrische Verfahren stellen bei unklaren Fällen die erweiterte Diagnostik dar. Neben der konservativen Therapie einer allergischen oder vasomotorischen Rhinitis mittels spezifischer Immuntherapie bzw. topischer Kortikoide gibt es diverse interventionelle Verfahren zur Verkleinerung des Muschelgewebes bei einem hohen Maß an Schonung der respiratorischen Schleimhaut.
http://ift.tt/2p57iUQ
Abrasion and blunt tissue trauma study of a novel flexible robotic system in the porcine model
Source:American Journal of Otolaryngology
Author(s): Michael Z. Lerner, Michael Tricoli, Marshall Strome
ObjectivesThe objective of this study was to determine if a flexible robotic system caused increased tissue reaction when accessing the oropharynx and hypopharynx compared to intubation controls in only 2 scenarios: high speed tissue impact and multiple unit insertions and retractions. The data obtained were submitted as part of the entirety of information submitted for FDA approval.MethodsThis study consisted of 5 groups of Yorkshire pigs (2 animals per group). On Day 0, all animals were intubated. For group 1 (control), a second endotracheal tube was advanced to just above the vocal cords. In abrasion groups 2 and 3, the flexible robotic system was advanced against the oropharyngeal and hypopharyngeal tissues, respectively. In blunt trauma groups 4 and 5, the flexible robotic system was advanced at maximum speed (22mm/s) to collide with oropharyngeal and hypopharyngeal tissues, respectively. Pre- and post-procedure endoscopic assessments of tissue reaction were performed daily for 4 days. An independent reviewer graded tissue reaction using a 0–3 point scale.ResultsTissue reaction scores at each observation time point for all test groups were less than or equal to control scores except for one instance of moderate scoring (2 out of 3) on Day 2 for an animal in the blunt trauma group where reaction was likely intubation-related rather than device impact related. Otherwise, all flexible robotic system-treated animal scores were less than 1 by Day 4.ConclusionsIn this limited study, the flexrobotic system afforded surgical access to the oropharynx and hypopharynx without an increased level of abrasion or tissue trauma when compared to intubation alone.
http://ift.tt/2o1D1ES
Immune-mediated cytokine storm and its role in severe dengue
Abstract
Dengue remains one of the most important mosquito-borne diseases worldwide. Infection with one of the serologically related dengue viruses (DENVs) can lead to a wide range of clinical manifestations and severity. Severe dengue is characterized by plasma leakage and abnormal bleeding that can lead to shock and death. There is currently no specific treatment for severe dengue due to gaps in understanding of the underlying mechanisms. The transient period of vascular leakage is usually followed by a rapid recovery and is suggestive of the effects of short-lived biological mediators. Both the innate and the adaptive immune systems are activated in severe dengue and contribute to the cytokine production. We discuss the immunological events elicited during a DENV infection and identify candidate cytokines that may play a key role in the severe manifestations of dengue and possible interventions.
http://ift.tt/2opOL7F
Maternal hypomagnesemia alters hippocampal NMDAR subunit expression and programs anxiety-like behaviour in adult offspring
Source:Behavioural Brain Research SreeTestContent1, Volume 328
Author(s): R.N. Schlegel, J.G. Spiers, K.M. Moritz, C.L. Cullen, S.T. Björkman, T.M. Paravicini
It is well established that maternal undernutrition and micronutrient deficiencies can lead to altered development and behaviour in offspring. However, few studies have explored the implications of maternal Mg deficiency and programmed behavioural and neurological outcomes in offspring. We used a model of Mg deficiency (prior to and during pregnancy and lactation) in CD1 mice to investigate if maternal Mg deficiency programmed changes in behaviour and NMDAR subunit expression in offspring. Hippocampal tissue was collected at postnatal day 2 (PN2), PN8, PN21 and 6 months, and protein expression of NMDAR subunits GluN1, GluN2A and GluN2B was determined. At 6 months of age, offspring were subject to behavioural tasks testing aspects of anxiety-like behaviour, memory, and neophobia. Maternal hypomagnesemia was associated with increased GluN1, GluN2A and GluN2B subunit expression in female offspring at 6 months, but decreased GluN1 and GluN2A expression in males. The GluN2B:GluN2A expression ratio was increased in both sexes. Male (but not female) offspring from Mg-deficient dams showed anxiety-like behaviour, with reduced head dips (Suok test), and reduced exploration of open arms (elevated plus maze). Both male and female offspring from Mg-deficient dams also showed impaired recognition memory (novel object test). These findings suggest that maternal Mg deficiency can result in behavioural deficits in adult life, and that these changes may be related to alterations in hippocampal NMDA receptor expression.
http://ift.tt/2owMeJ8
The Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms
Publication date: May 2017
Source:The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry, Volume 117, Issue 5, Supplement
http://ift.tt/2o1T05B
Adaptive and maladaptive neural compensatory consequences of sensory deprivation—From a phantom percept perspective
Source:Progress in Neurobiology
Author(s): Anusha Mohan, Sven Vanneste
It is suggested that the brain undergoes plastic changes in order to adapt to changing environmental needs. Sensory deprivation results in decreased input to the brain leading to adaptive or maladaptive changes. Although several theories hypothesize the mechanism of these adaptive and maladaptive changes, the course of action taken by the brain heavily depends on the age of incidence of damage. The growing body of literature on the topic proposes that maladaptive changes in the brain are instrumental in creating phantom percepts, defined as the perception of a sensory experience in the absence of a physical stimulus. The current article reviews the mechanisms of adaptive and maladaptive plasticity in the brain in congenital, early, and late-onset sensory deprivation in conjunction with the phantom percepts in the different sensory domains. We propose that the mechanisms of adaptive and maladaptive plasticity fall under a universal construct of updating hierarchical Bayesian prediction errors. This theory of the Bayesian brain hypothesizes that the brain constantly compares its internal milieu with changing environmental cues and either adjusts its predictions or discards the change, depending on the novelty or salience of the external stimulus. We propose that adaptive plasticity reflects both successful bottom-up compensation and top-down updating of the model while maladaptive plasticity reflects failure in one or both mechanisms, resulting in a constant prediction-error. Finally, we hypothesize that phantom percepts are generated by the brain as a solution to this prediction error and are thus a manifestation of unsuccessful adaptation to sensory deprivation.
http://ift.tt/2p2ZGVH
Influence of N-acetyl cysteine on beta-amyloid-induced Alzheimer’s disease in a rat model: A behavioral and electrophysiological study
Source:Brain Research Bulletin
Author(s): Siamak Shahidi, Somayeh Zargooshnia, Sara Soleimani Asl, Alireza Komaki, Abdolrahman Sarihi
Alzheimer's disease is an age-related neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a progressive decline in cognitive function due to the extracellular accumulation and deposition of beta-amyloid peptide (Aβ). The purpose of this study was to evaluate the protective effect of N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) on learning and memory in an Aβ-induced Alzheimer's disease model in adult male rats, using behavioral and electrophysiological methods Thirty-five rats were divided into five groups: control, sham-operated, Aβ, Aβ+NAC (1–14 days), and Aβ+NAC (14–28 days). Learning and memory were evaluated behaviorally using the passive avoidance test and electrophysiologically by assessing hippocampal long-term potentiation, a cellular mechanism of learning and memory. Intrahippocampal Aβ injections reduced step-through latency in the passive avoidance test, and decreased both the amplitude of hippocampal neuron population spikes and the slope of excitatory postsynaptic potentials, compared to the sham and control groups. Administration of NAC in rats receiving Aβ alleviated the Aβ-induced deficits in comparison to the Aβ-only group. The results of this study suggest that NAC shows potential for treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
http://ift.tt/2p2GLdC
Primary Extracranial Meningioma: A Rare Location
Abstract
Meningiomas are benign extraaxial tumors of the central nervous system (CNS). Extracranial meningiomas are extremely rare (2%) and can develop as a direct extension from a primary intracranial meningioma or as true primary extracranial meningioma originating from ectopic arachnoid cells. Only eight cases of primary meningioma in the jaw have been reported to date. Extracranial meningiomas are frequently misdiagnosed, resulting in inappropriate clinical management. The aim of this article was to describe the case of a man with an asymptomatic swelling in the right retromolar area over a period of 2 months. Cone beam computed tomography was performed to determine the extension and involvement of the adjacent structures. Histopathological findings and immunohistochemical analysis aided in the diagnosis of primary extracranial meningioma in the mandible and several aspects of this unusual neoplasm are reviewed. The treatment of choice was a partial resection of the mandible and reconstruction with autogenous iliac tricortical bone. Five years after surgery, the patient remains free of disease.
http://ift.tt/2p41Emb
Primary Extracranial Meningioma: A Rare Location
Abstract
Meningiomas are benign extraaxial tumors of the central nervous system (CNS). Extracranial meningiomas are extremely rare (2%) and can develop as a direct extension from a primary intracranial meningioma or as true primary extracranial meningioma originating from ectopic arachnoid cells. Only eight cases of primary meningioma in the jaw have been reported to date. Extracranial meningiomas are frequently misdiagnosed, resulting in inappropriate clinical management. The aim of this article was to describe the case of a man with an asymptomatic swelling in the right retromolar area over a period of 2 months. Cone beam computed tomography was performed to determine the extension and involvement of the adjacent structures. Histopathological findings and immunohistochemical analysis aided in the diagnosis of primary extracranial meningioma in the mandible and several aspects of this unusual neoplasm are reviewed. The treatment of choice was a partial resection of the mandible and reconstruction with autogenous iliac tricortical bone. Five years after surgery, the patient remains free of disease.
http://ift.tt/2p41Emb
The state of asthma epidemiology: an overview of systematic reviews and their quality
Recently, we have published an overview of systematic reviews in allergy epidemiology and identified asthma as the most commonly reviewed allergic disease. Building on this work, we aimed to investigate the qu...
http://ift.tt/2pqCHjV
The state of asthma epidemiology: an overview of systematic reviews and their quality
Recently, we have published an overview of systematic reviews in allergy epidemiology and identified asthma as the most commonly reviewed allergic disease. Building on this work, we aimed to investigate the qu...
http://ift.tt/2pqCHjV
Tumor-associated myeloid cells as guiding forces of cancer cell stemness
Abstract
Due to their ability to differentiate into various cell types and to support tissue regeneration, stem cells simultaneously became the holy grail of regenerative medicine and the evil obstacle in cancer therapy. Several studies have investigated niche-related conditions that favor stemness properties and increasingly emphasized their association with an inflammatory environment. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are major orchestrators of cancer-related inflammation, able to dynamically express different polarized inflammatory programs that promote tumor outgrowth, including tumor angiogenesis, immunosuppression, tissue remodeling and metastasis formation. In addition, these myeloid populations support cancer cell stemness, favoring tumor maintenance and progression, as well as resistance to anticancer treatments. Here, we discuss inflammatory circuits and molecules expressed by TAMs and MDSCs as guiding forces of cancer cell stemness.
http://ift.tt/2ooIqJj
Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2023
(391)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (200)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (191)
-
►
2022
(2843)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (161)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (219)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (264)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (280)
-
►
2021
(5625)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (231)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (345)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (620)
-
►
2020
(2065)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (535)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (222)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (28)
-
►
2019
(9608)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (19)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (3791)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (3737)
-
►
2018
(69720)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (3507)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (3851)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (8116)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (7758)
-
▼
2017
(111579)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (7718)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (7549)
-
▼
Απριλίου
(11636)
-
▼
Απρ 11
(422)
- Vision Loss, Rash, and Abnormal Brain Magnetic Res...
- Analyzing interactions on combining multiple clini...
- Two cases with an interseptal sinus cell mucocele:...
- One-lung ventilation using a bronchial blocker tub...
- Issue Information - Journal Info page
- Issue Information - TOC
- Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma with Cystic Cervical Meta...
- Subcutaneous Emphysema, Pneumomediastinum and Pneu...
- Tapia's Syndrome after Corrective Jaw Surgery unde...
- Extranodal NK/T Cell Lymphoma with Destruction of ...
- Report of Common Aeroallergens among Allergic Pati...
- Outcome of Incus Interposition after Preservation ...
- Otitis Media with Effusion in Children and the Imp...
- The Effect of Topical Tranexamic Acid on Bleeding ...
- Comparison of Temporalis Fascia and Full-Thickness...
- CYCORE: Cyberinfrastructure for Comparative Effect...
- Survey Study and Records Review of Treatment Outco...
- Anti-inflammatory, antimycobacterial and genotoxic...
- Anti-inflammatory activity of Crateva adansonii DC...
- CYCORE: Cyberinfrastructure for Comparative Effect...
- Survey Study and Records Review of Treatment Outco...
- Neue Therapieoption bei Acne vulgaris
- Narben effektiv behandeln
- Mit Nadeln gegen Narben
- Haartransplantation
- Neue Optionen der Teamarbeit in Kommunen
- Dermatokosmetika bei Akne: Was ist empfehlenswert?
- ADK aktiv bei dermatologischen Fortbildungen
- Tagung Dermatologische Praxis 2017
- Zytologie in der dermatologischen Praxis
- Mustervorlage für Hygieneplan
- Atopisches Ekzem: Proaktiv behandeln!
- Wasserlöslicher Nagellack
- Nicht invasives Lifting
- Inhaltsverzeichnis
- Die Adhärenz junger Akne-Patienten verbessern — ab...
- Pigmentverändungen vorbeugen
- Sterbegeld muss versteuert werden
- Lichttherapie gegen Juckreiz: UV-B nicht mit UV-A ...
- „Es klappt ja doch mit Familie!“
- „Ganzkörper-Lichttherapie oft zu früh abgesetzt“
- Stem cell delivery in tissue-specific hydrogel ena...
- Plasmonic titanium nitride nanoparticles for in vi...
- Vaccine nanocarriers: Coupling intracellular pathw...
- Local induction of lymphangiogenesis with engineer...
- Free Recall Test Experience Potentiates Strategy-D...
- Long-Term Memory Biases Auditory Spatial Attention.
- Abrupt Strategy Change Underlies Gradual Performan...
- Does Testing Increase Spontaneous Mediation in Lea...
- Novel thyroid hormone analogues, enzyme inhibitors...
- Nutritional approaches for managing obesity-associ...
- On “Cleft relapse and oronasal fistula after Furlo...
- “Rare place where I feel normal”: Perceptions of a...
- A randomized clinical trial about presence of path...
- Erratum to: Chronic hyperglycemia affects bone met...
- Contemporary surgical management of hypodontia
- New technique for midpalatal osteotomy in surgical...
- Bilateral submandibular rhabdomyomas: case report
- Surgeon-Reported Needs for Improved Training in Id...
- Reply
- Serum IgE as biomarker for predicting allergen imm...
- Novel Morpheme Learning in Monolingual and Bilingu...
- Calculus migration characterization during Ho:YAG ...
- Chirurgische Prävention hereditärer gastrointestin...
- Brain Activity During Phonation in Women With Musc...
- Temporal abundance and activity trends of vinyl ch...
- Phytotoxicity of CeO 2 nanoparticles on radish pla...
- The role of forest in mitigating the impact of atm...
- Enzyme-based solutions for textile processing and ...
- Revisiting inland hypoxia: diverse exceedances of ...
- Dysregulated homeostasis of target tissues or auto...
- Dysregulated homeostasis of target tissues or auto...
- Identification of a novel missence mutation in FGF...
- Mutation analysis of common GJB2, SCL26A4 and 12S ...
- Inverse relationship between toxic shock syndrome ...
- HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DQB1 Alleles in Chinese Han Patie...
- Pediatric sialolithiasis is not related to oral or...
- A fatal case of Gradenigo’s Syndrome in Zimbabwe a...
- Correlation of frontal sinus recess anatomy with e...
- Abrasion and blunt tissue trauma study of a novel ...
- Improving resident familiarity with the translabyr...
- Assessing cumulative acute toxicity of chemoradiot...
- Primary Extracranial Meningioma: A Rare Location
- Correlation of frontal sinus recess anatomy with e...
- Abrasion and blunt tissue trauma study of a novel ...
- Improving resident familiarity with the translabyr...
- Assessing cumulative acute toxicity of chemoradiot...
- Successful one-lung ventilation using a bronchial ...
- Clinical Thyroidology for the Public – Highlighted...
- Clinical Thyroidology for the Public – Highlighted...
- Phonological Process Occurrence in Typically Devel...
- CD11b regulates antibody class switching via induc...
- Positive feedback effect of PGE2 on cyclooxygenase...
- Lichtschutzfaktor 50+
- Dithranol
- Lichtschutz bei Xeroderma pigmentosum
- Erratum zu: Orale Schleimhautalteration – was ist ...
- Nasenmuschelchirurgie
- CD11b regulates antibody class switching via induc...
- Positive feedback effect of PGE2 on cyclooxygenase...
-
▼
Απρ 11
(422)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (10753)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (10529)
-
►
2016
(16402)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (7478)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (900)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (1250)