|
Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2023
(391)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (200)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (191)
-
►
2022
(2843)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (161)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (219)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (264)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (280)
-
►
2021
(5625)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (231)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (345)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (620)
-
▼
2020
(2065)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (535)
-
▼
Νοεμβρίου
(733)
-
▼
Νοε 12
(33)
- Analysis of a Fractional Reaction-Diffusion HBV Mo...
- Using the Robson Classification to Explain the Flu...
- Maternal Deaths due to Obstetric Haemorrhage in Do...
- Can Mobile Technology Help Prevent the Burden of D...
- Lifetime Duration of Exposure to Biomechanical Fac...
- Genome‐wide search for genes affecting the age at ...
- Application of spectral CT in the diagnosis of con...
- Vaccines, Vol. 8, Pages 673: SARS-CoV-2 Proteins I...
- Metastatic Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor ...
- Vaccines, Vol. 8, Pages 674: The Impact of Serotyp...
- Validation of a Modified CDC Assay and Performance...
- Vaccines, Vol. 8, Pages 675: Association between E...
- Vaccines, Vol. 8, Pages 676: Multiple Vaccinations...
- Inner retinal dehiscence and macular microhole sec...
- Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis that spontaneo...
- An Exploratory Study of the Relative Effects of Va...
- The Need for Ocular Protection for Health Care Wor...
- Protocol for a case-control study of vitamin D sta...
- Fibrosis-4 index as a predictor for mortality
- Prevalence and predictors of poor sexual well-bein...
- Comparing intranasal 1.4 mg to intramuscular 0.8 m...
- Translating the Symptom Screening in Paediatrics T...
- Treatment with the anti-IgE monoclonal antibody om...
- Thromboelastography-guided blood transfusion durin...
- Life-threatening corrosive injury with hepato-rena...
- Antithrombotic therapy and the risk of new-onset d...
- The starry sky of tuberculoma
- Cystinuria
- Haemolytic crisis of hereditary spherocytosis
- Effects of the Mediterranean diet adherence on bod...
- Improving postoperative mobilisation rates in pati...
- 'The photographic negative of pulmonary oedema in ...
- Iatrogenic extracranial internal carotid artery an...
-
▼
Νοε 12
(33)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (222)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (28)
-
►
2019
(9608)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (19)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (3791)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (3737)
-
►
2018
(69720)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (3507)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (3851)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (8116)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (7758)
-
►
2017
(111579)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (7718)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (7549)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (10753)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (10529)
-
►
2016
(16402)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (7478)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (900)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (1250)
! # Ola via Alexandros G.Sfakianakis on Inoreader
Η λίστα ιστολογίων μου
Πέμπτη 12 Νοεμβρίου 2020
Analysis of a Fractional Reaction-Diffusion HBV Model with Cure of Infected Cells
Using the Robson Classification to Explain the Fluctuations in Cesarean Section
|
Maternal Deaths due to Obstetric Haemorrhage in Dodoma Regional Referral Hospital, Tanzania
|
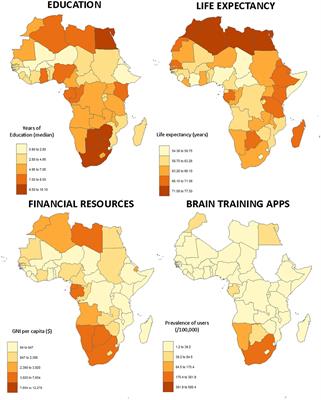
Can Mobile Technology Help Prevent the Burden of Dementia in Low- and Mid-Income Countries?
|
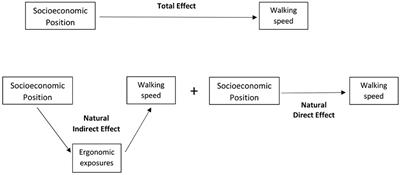
Lifetime Duration of Exposure to Biomechanical Factors at Work as a Mediator of the Relationship Between Socioeconomic Position and Walking Speed
|
Genome‐wide search for genes affecting the age at diagnosis of type 1 diabetes
|
Application of spectral CT in the diagnosis of contrast encephalopathy following carotid artery stenting: a case report
|
Vaccines, Vol. 8, Pages 673: SARS-CoV-2 Proteins Induce IFNG in Th1 Lymphocytes Generated from CD4+ Cells from Healthy, Unexposed Polish Donors
|
Metastatic Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive Breast Cancer: Current Treatment Standards and Future Perspectives
|
Vaccines, Vol. 8, Pages 674: The Impact of Serotype Cross-Protection on Vaccine Trials: DENVax as a Case Study
|
Validation of a Modified CDC Assay and Performance Comparison with the NeuMoDx™ and DiaSorin® automated assays for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Respiratory Specimens
|
Vaccines, Vol. 8, Pages 675: Association between Exposure to Influenza Vaccination and COVID-19 Diagnosis and Outcomes
|
Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2023
(391)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (200)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (191)
-
►
2022
(2843)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (161)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (219)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (264)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (280)
-
►
2021
(5625)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (231)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (345)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (620)
-
▼
2020
(2065)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (535)
-
▼
Νοεμβρίου
(733)
-
▼
Νοε 12
(33)
- Analysis of a Fractional Reaction-Diffusion HBV Mo...
- Using the Robson Classification to Explain the Flu...
- Maternal Deaths due to Obstetric Haemorrhage in Do...
- Can Mobile Technology Help Prevent the Burden of D...
- Lifetime Duration of Exposure to Biomechanical Fac...
- Genome‐wide search for genes affecting the age at ...
- Application of spectral CT in the diagnosis of con...
- Vaccines, Vol. 8, Pages 673: SARS-CoV-2 Proteins I...
- Metastatic Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor ...
- Vaccines, Vol. 8, Pages 674: The Impact of Serotyp...
- Validation of a Modified CDC Assay and Performance...
- Vaccines, Vol. 8, Pages 675: Association between E...
- Vaccines, Vol. 8, Pages 676: Multiple Vaccinations...
- Inner retinal dehiscence and macular microhole sec...
- Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis that spontaneo...
- An Exploratory Study of the Relative Effects of Va...
- The Need for Ocular Protection for Health Care Wor...
- Protocol for a case-control study of vitamin D sta...
- Fibrosis-4 index as a predictor for mortality
- Prevalence and predictors of poor sexual well-bein...
- Comparing intranasal 1.4 mg to intramuscular 0.8 m...
- Translating the Symptom Screening in Paediatrics T...
- Treatment with the anti-IgE monoclonal antibody om...
- Thromboelastography-guided blood transfusion durin...
- Life-threatening corrosive injury with hepato-rena...
- Antithrombotic therapy and the risk of new-onset d...
- The starry sky of tuberculoma
- Cystinuria
- Haemolytic crisis of hereditary spherocytosis
- Effects of the Mediterranean diet adherence on bod...
- Improving postoperative mobilisation rates in pati...
- 'The photographic negative of pulmonary oedema in ...
- Iatrogenic extracranial internal carotid artery an...
-
▼
Νοε 12
(33)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (222)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (28)
-
►
2019
(9608)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (19)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (3791)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (3737)
-
►
2018
(69720)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (3507)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (3851)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (8116)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (7758)
-
►
2017
(111579)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (7718)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (7549)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (10753)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (10529)
-
►
2016
(16402)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (7478)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (900)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (1250)