Clinical Balance Testing to Screen for Patients With Vestibular Disorders: A Retrospective Case-control Study:

Interventions:
All subjects performed Romberg and Jendrassic maneuver with eyes closed (ROMJec), standing on foam with eyes open (SOFeo) and eyes closed (SOFec), Tandem Romberg with eyes open (TReo) and eyes closed (TRec), single leg stance with eyes open (SLSeo) and eyes closed (SLSec), Tandem gait (TG) and Timed Up and Go (TUG).----
The patient starts in a seated position
The patient stands up upon therapist’s command: walks 3 meters, turns around, walks back to the chair and sits down.
The time stops when the patient is seated.
The subject is allowed to use an assistive device. Be sure to document the assistive device used.
Tandem gait is a gait (method of walking or running) where the toes of the back foot touch the heel of the front foot at each step. Neurologists sometimes ask patients to walk in a straight line using tandem gait as a test to help diagnose ataxia, especially truncal ataxia, because sufferers of these disorders will have an unsteady gait. However, the results are not definitive, because many disorders or problems can cause unsteady gait (such as vision difficulties and problems with the motor neurons or associative cortex). Therefore, inability to walk correctly in tandem gait does not prove the presence of ataxia.
Profoundly affected tandem gait with no other perceptible deficits is a defining feature of posterior vermal split syndrome.[1]
Suspects may also be asked to perform a tandem gait walk during the "walk and turn" part of a field sobriety test.[2]
Main outcome measures:
Significant differences in performance on the balance tests.
Results:
For the age-group <40 years, TUG >6 seconds (OR 102.4; p <0.0001) and SLSec <30 seconds (OR 48.0; p <0.0001) proved to be the most predictive combination of testing (AUC 0.9; LR+ 15.8; LR− 0.2), with a positive predictive value (PPV) of 88.4%. For the age-group 40–60, TUG >7 seconds (OR 4.0; p = 0.0107) and TRec <30 seconds (OR 63.1; p < 0.0001) was the most predictive combination of tests (AUC 0.9 LR+ 6.0; LR− 0.1), with a PPV of 93.8%. For the age-group >60 the combination of TUG >8 seconds (OR 17.4; p < 0.0001) and SOFec <30 seconds (OR 10.4; p < 0.0001) was the most predictive (AUC 0.9 LR+ 6.3; LR− 0.2), with a PPV of 84.8%.
Conclusions:
Combinations of clinical tests are proposed to promptly screen for vestibular disorders in specific age groups. To interpret the results for the individual patient, the physician must take the history and the general examination into consideration.
Romberg Test
Related online courses on +Physioplus
Online Course: Shoulder Assessment
Online Course: Vestibular and Oculomotor Assessment
Online Course: Parkinson’s Outcome Measures Case Study
Introduction
The Romberg test is an appropriate tool to diagnose sensory ataxia, a gait disturbance caused by abnormal proprioception involving information about the location of the joints. It is also proven to be sensitive and accurate means of measuring the degree of disequilibrium caused by central vertigo, peripheral vertigo and head trauma.[1] It has been used in clinic for 150 years [2]
Purpose
The Romberg test is used to demonstrate the effects of posterior column disease upon human upright postural control. Posterior column disease involves selective damaging of the posterior column, known as tabes dorsalis neurosyphilis. The Romberg test is used for the clinical assessment of patients with disequilibrium or ataxia from sensory and motor disorders.
Equilibrium is defined as any condition in which all acting forces are cancelled by each other resulting in a stable balanced system. It is maintained through the sensory information from vestibular, somatosensory and visual systems. A patient who has a problem with Proprioception (Somatosensory) can still maintain balance by compensating with vestibular function and vision. In the Romberg test, the patient stands upright and asked to close his eyes. A loss of balance is interpreted as a positive Romberg sign.
The Romberg test was first described in 1846 and was originally described for the condition tabes dorsalis. Before performing the Romberg test, it is necessary to test other aspects of the patient's balance when potential issues with ataxia or disequilibrium are present. Often, proprioceptive challenges are not the first problems faced by this population. Sometimes, it is more simple. It is important to first assess other aspects of balance impairment in order to rule out confounding factors that could lead to a false positive test[3][4].
Clinically Relevant Anatomy
There are three sensory systems that provide input to the cerebellum to maintain truncal stability when the eyes are open:
Vision
Proprioception
Vestibular sense
Only two of the three systems are needed to maintain balance. When visual input is removed, instability due to lack of vision can be teased apart from other sensory impairments. If there is a more severe proprioceptive or vestibular lesion, or if there is a midline cerebellar lesion causing truncal instability, the patient will be unable to maintain the standing position, even when the eyes are open. Note that instability can also be seen with lesions in other parts of the nervous system, such as the upper or lower motor neurons, or the basal ganglia[5][6].
Technique
The Original Romberg test
The test is performed as follows:
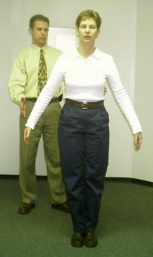
The patient is asked to remove his shoes and stand with his two feet together. The arms are held next to the body or crossed in front of the body.
The clinician asks the patient to first stand quietly with eyes open, and subsequently with eyes closed. The patient tries to maintain his balance. For safety, it is essential that the observer stand close to the patient to prevent potential injury if the patient were to fall. When the patients closes his eyes, he should not orient himself by light, sense or sound, as this could influence the test result and cause a false positive outcome.
The Romberg test is scored by counting the seconds the patient is able to stand with eyes closed.
The literature does not report alternative methods for scoring a Romberg test.
To make the Romberg test more difficult, the clinician can attempt to disturb the patient's balance with a perturbation. It is important that the clinician does not exaggerate the perturbation.
A Romberg test can also be used as follow-up assessment for patients with balance and/or proprioception impairments by comparing several different assessments with each other.
If the clinician observes that the patient is able to stand for longer periods of time with the eyes closed, it is evident that the patient's balance and proprioceptive deficits have decreased[3][7][4][8].
The Romberg test is positive when the patient is unable to maintain balance with their eyes closed. Losing balance can be defined as increased body sway, placing one foot in the direction of the fall, or even falling.
The Sharpened or Tandem Romberg test
The Sharpened or Tandem Romberg test is a variation of the original test. The implementation is mostly the same. For this second test, the patient has to place his feet in heel-to-toe position, with one foot directly in front of the other. As with the original Romberg test, the assessment is performed first with eyes open and then with eyes closed. The patient crosses his arms over his chest, and the open palm of the hand lies on the opposite shoulder. The patient also distributes his weight over both his feet and holds his chin parallel with the floor[7][4].
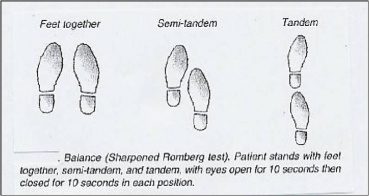
Obese and older individuals may be unable to stand in this position for prolonged periods of time. For these populations, the Romberg test does not exclusively demonstrate proprioceptive impairments in comparison to other confounding factors[3].
Variables
Although a patient with an acute peripheral vestibular lesion is usually inclined to move towards the side of the problem, it has been shown that chronic vestibular damage (at least partial compensation) does not produce deficits in the standard Romberg test. As well, an individual with proprioceptive problems, accessory to tabes dorsalis, would be unable to stand with the eyes closed and feet together[3].
Many believe that the sharpened Romberg test is a better indicator of vestibular impairment than the original Romberg test. The sharpened Romberg test results give an objective measure of postural stability. This can help to quantify ataxia[3].
Subject, sex, and age do not create a statistically significant difference between normal subjects between the ages of 20 and 49 years; only the Romberg sharpened test with eyes open provided a significant difference (p< 0.05) between men and women. Greater instability in subjects less than 20 and more than 50 years of age was also exhibited. When comparing a young and an old cohort, there is a significant difference in performance.
Increasing the difficulty of the tandem Romberg test for patients is not helpful because it also makes the tests more difficult to perform for controls with no symptoms of vestibular disease. This would also make it harder to evaluate the test results. Decreased performance times on the modified Romberg is associated with a concomitant rise in the risk of falling[4][9][10].
Reliability and Validity
There is no consensus in the Reliability (Intra and inter) and validity for Romberg's in the literature as the test is more of qualitative rather than quantitative (Objective). However, this test can be used as a quick clinical tool to screen. The introduction of various instrument in the arena of balance assessment and the force platform usage has given the more objective and accurate measurement.
Limitations[11] [12]
Not Quantitative
Low diagnostic sensitivity and specificity
Low power to determine lesions, predict the risk of falling and reflect the discomfort and ability to perform daily activities.
Δεν υπάρχουν σχόλια:
Δημοσίευση σχολίου